
H1702 CTF was a great event organized by hackerone. Participants had to find 12 flags in Android and iOS reverse engineering challenges. I’m going to present my solutions in this post.

I finished the competition in 1st place 😃
Thanks hackerone for this awesome CTF!
Android Writeups
Level 1
Let's start you off with something easy to get you started.
(Note: Levels 1-4 use the same application)
ctfone-490954d49dd51911bc730d8161541cf13e7416f9.apk
I started Android Emulator (armv7 AVD) and installed the APK.
➜ adb install ~/Downloads/ctfone-490954d49dd51911bc730d8161541cf13e7416f9.apk
I opened the app and realized that if the EditText was empty, some random assets were loaded after clicking the LOAD ASSET button.

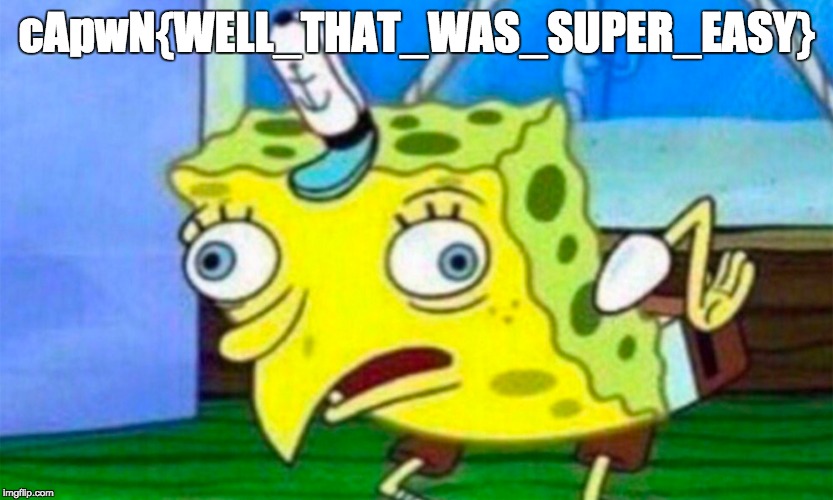
So, I extracted the APK and found an interesting file named tHiS_iS_nOt_tHE_SeCrEt_lEveL_1_fiLE inside the assets folder. It was just a JPEG image containing the first flag.

Level 2
Maybe something a little more difficult?
Let’s take a look on the second tab:
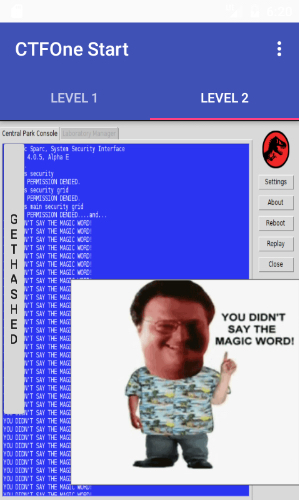
If we click on the GETHASHED button we got a hash.
➜ Static Analysis
I decompiled the APK using JADX and inspected the TabFragment2.java code.
TabFrament2.java
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class TabFragment2 extends Fragment {
TextView mHashView;
class C02241 implements OnClickListener {
C02241() {
}
public void onClick(View v) {
try {
TabFragment2.this.mHashView.setText(InCryption.hashOfPlainText());
TabFragment2.this.mHashView.setBackgroundColor(-1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View v = inflater.inflate(C0222R.layout.tag_fragment2, container, false);
this.mHashView = (TextView) v.findViewById(C0222R.id.hashText);
((Button) v.findViewById(C0222R.id.hashmebutton)).setOnClickListener(new C02241());
return v;
}
}
The hash is computed by the function hashOfPlainText in the InCryption class.
InCryption.java (click to expand)
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class InCryption {
static String encryptedHex = "ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f128bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c97c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ae151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b2ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b483469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a00d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91fca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e4be535b1314ecb6fb99b3985c06ae00616288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ae151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b2ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c9828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711e151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b2ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c97c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f950d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed9186622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff2244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbadfca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e4be535b1314ecb6fb99b3985c06ae00616288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc79ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277a2757324dfeeb647dd2ab010b91af0bd3ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c98bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a339ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277a3cad3497d53b3c22fdd26fbb83f5cae8fe5f529bf234dcef4e76913394ae8f85244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbade57dded1cc4a151b2da4b3fa1041bc7f569f11fcae23f0661a6722466e5697ce069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ae151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b29a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd89a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8d5a6b3cf8313ced4ca89414d00adb0c2a854ed5338d047e0b65b956bd2a19fcc0d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba0714e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba071486622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff216288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e299ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277a4be535b1314ecb6fb99b3985c06ae00616288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e299a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b48ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ac9dcd54eb33f50a80149e8457d843b84ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abde5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b87b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd33cad3497d53b3c22fdd26fbb83f5cae82d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b10ea54646c339600f167b5dd2029ba72fe5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b5762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b69e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba07147c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc7ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95c8dab6841e142338fcc2d01ad0a3bce686622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff216288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f950d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91fca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e0f1f25bef4b7f6442b420b861ad834aac8dab6841e142338fcc2d01ad0a3bce67c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a03469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a00d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba071486622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff2244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbad828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711e151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b29a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8d5a6b3cf8313ced4ca89414d00adb0c22d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c9828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711c9dcd54eb33f50a80149e8457d843b845bd9ba2fb7cea981a019c784939dfd0587b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd328d63f46073aec9a139375fd6d2917d3e5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b87b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd30f1f25bef4b7f6442b420b861ad834aa41c1b4f70e10af5fa9e82a2b773ea7070ea54646c339600f167b5dd2029ba72fe5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b5762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b697c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a05bd9ba2fb7cea981a019c784939dfd055762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b69e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba0714fca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e2757324dfeeb647dd2ab010b91af0bd3ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c9828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711e151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b29a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8d5a6b3cf8313ced4ca89414d00adb0c2fc59c44e8f481760ef82750176f42291fb7648043fce2338843c67eae566b35c8bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f12828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a3571116d696017b13e85d5aaf28d6ac7c3d315762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b698bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a339a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b48ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b48c8dab6841e142338fcc2d01ad0a3bce67c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1a25c129f9071f52f674b28cff9f4ade7244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbade891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba0714828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711c9dcd54eb33f50a80149e8457d843b843d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc7e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abd569f11fcae23f0661a6722466e5697ce9ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277abea40e40b98659cafe52c74461e7015a87b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd33cad3497d53b3c22fdd26fbb83f5cae8fe5f529bf234dcef4e76913394ae8f8516288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abd31e2e92c15e8b3afb3b4a4344f6d37a33d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc7e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abd31e2e92c15e8b3afb3b4a4344f6d37a341c1b4f70e10af5fa9e82a2b773ea707a25c129f9071f52f674b28cff9f4ade7244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbad011d2d66c36261ef7fb7ca949a22ed84";
public static String hashOfPlainText() throws Exception {
return getHash(new String(hex2bytes(new String(decrypt(hex2bytes("0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF"), hex2bytes(encryptedHex))).trim())));
}
private static byte[] decrypt(byte[] raw, byte[] encrypted) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(raw, "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(2, skeySpec);
return cipher.doFinal(encrypted);
}
public static String getHash(String text) {
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
digest.reset();
return bin2hex(digest.digest(text.getBytes()));
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
return "";
}
}
static byte[] hex2bytes(String s) {
byte[] b = new byte[(s.length() / 2)];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
int index = i * 2;
b[i] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(s.substring(index, index + 2), 16);
}
return b;
}
static String bin2hex(byte[] data) {
return String.format("%0" + (data.length * 2) + "X", new Object[]{new BigInteger(1, data)});
}
}
Basically, the decrypt function is called with the arguments hex2bytes("0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF") and hex2bytes(encryptedHex). The computed SHA256 hash is the hash of the plaintext. The cipher used was AES in ECB mode with PKCS5 padding. I implemented the decrypt function in python:
decrypt.py (click to expand)
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
pkcs5_unpad = lambda s : s[0:-ord(s[-1])]
key = "0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF".decode("hex")
ciphertext = "ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f128bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c97c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ae151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b2ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b483469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a00d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91fca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e4be535b1314ecb6fb99b3985c06ae00616288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ae151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b2ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c9828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711e151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b2ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c97c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f950d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed9186622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff2244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbadfca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e4be535b1314ecb6fb99b3985c06ae00616288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc79ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277a2757324dfeeb647dd2ab010b91af0bd3ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c98bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a339ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277a3cad3497d53b3c22fdd26fbb83f5cae8fe5f529bf234dcef4e76913394ae8f85244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbade57dded1cc4a151b2da4b3fa1041bc7f569f11fcae23f0661a6722466e5697ce069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ae151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b29a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd89a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8d5a6b3cf8313ced4ca89414d00adb0c2a854ed5338d047e0b65b956bd2a19fcc0d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba0714e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba071486622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff216288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e299ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277a4be535b1314ecb6fb99b3985c06ae00616288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e299a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b48ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25069590e37f53bebf7c16b617482a4b8ac9dcd54eb33f50a80149e8457d843b84ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abde5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b87b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd33cad3497d53b3c22fdd26fbb83f5cae82d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b10ea54646c339600f167b5dd2029ba72fe5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b5762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b69e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba07147c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc7ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95c8dab6841e142338fcc2d01ad0a3bce686622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff216288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f950d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91fca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e0f1f25bef4b7f6442b420b861ad834aac8dab6841e142338fcc2d01ad0a3bce67c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a03469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a00d0d3f3cb085730e3335b7170a03ed91e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba071486622d5215afd9192d1b553cba233ff2244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbad828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711e151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b29a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8d5a6b3cf8313ced4ca89414d00adb0c22d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c9828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711c9dcd54eb33f50a80149e8457d843b845bd9ba2fb7cea981a019c784939dfd0587b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd328d63f46073aec9a139375fd6d2917d3e5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b87b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd30f1f25bef4b7f6442b420b861ad834aa41c1b4f70e10af5fa9e82a2b773ea7070ea54646c339600f167b5dd2029ba72fe5beb88aa4073a5c948816378f2cc96b5762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b697c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f953469118ed906f6b3abeff55bcdc7e5a05bd9ba2fb7cea981a019c784939dfd055762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b69e891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba0714fca1309cccb8078e2a9100cbbeaff61e2757324dfeeb647dd2ab010b91af0bd3ad074d17c3a227d487c85b88487435c9828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711e151286044c2a8237302612c7d88c8b29a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8d5a6b3cf8313ced4ca89414d00adb0c2fc59c44e8f481760ef82750176f42291fb7648043fce2338843c67eae566b35c8bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a33ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f12828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a3571116d696017b13e85d5aaf28d6ac7c3d315762452778b31d42ead4f81062775b698bb0552673171d078cc2e6b191b4cbaa2d8c5c0bb95e29cee0cb0ea0db961a339a4ef6d9c9cf8127de64c59ecc865fd8ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b48ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1d764b219e31def9c556a602e6b236b48c8dab6841e142338fcc2d01ad0a3bce67c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25ce0eef96ce210effc6a2733a73b371b1a25c129f9071f52f674b28cff9f4ade7244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbade891d349f90afb2d3f9608a7cdba0714828b8963fd132831a1f74db480a35711c9dcd54eb33f50a80149e8457d843b843d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc7e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abd569f11fcae23f0661a6722466e5697ce9ef39beaabf2ba23780e727eeb4e277abea40e40b98659cafe52c74461e7015a87b18c9563646c0652a9efd72f29cdd33cad3497d53b3c22fdd26fbb83f5cae8fe5f529bf234dcef4e76913394ae8f8516288270b1670f7bf609b8c9c3d62e29ec49822b5417f4dad5d6048804c07f127c3f9992b1a3d08f43fc92f416820f95ba463a67b09eb3433fb94ce2d2c5ac25e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abd31e2e92c15e8b3afb3b4a4344f6d37a33d255754f0e4004ac69e2e9b2e35ebc7e6ff67049d59429fa81ea1d14e1a4abd31e2e92c15e8b3afb3b4a4344f6d37a341c1b4f70e10af5fa9e82a2b773ea707a25c129f9071f52f674b28cff9f4ade7244ded87c4d06dd82895f2b20110bbad011d2d66c36261ef7fb7ca949a22ed84".decode("hex")
cipher = AES.new(key)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
dec = pkcs5_unpad(plaintext).rstrip().decode("hex")
print(dec)
Now we have the following plaintext, after decoding it as hex, since hex2bytes is called after decrypt:
DASH DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DASH SPACE DOT DASH DASH DOT SPACE DOT DASH DASH SPACE DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DOT DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DASH SPACE DASH DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DASH SPACE DOT SPACE DASH SPACE DASH DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DASH DASH SPACE DOT DASH DASH DOT SPACE DASH DASH DOT DOT DOT SPACE DASH DASH DASH DASH DASH SPACE DASH DOT DOT DOT DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DOT DOT DOT DASH SPACE DOT DASH DASH DOT SPACE DOT DOT DOT DOT SPACE DASH DOT DASH DASH SPACE DOT DOT DASH SPACE DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DOT SPACE DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DOT DOT SPACE DASH DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DASH DASH SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT SPACE DOT DASH DASH DASH DASH SPACE DOT DOT DOT DOT DOT SPACE DOT DOT DASH SPACE DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DOT SPACE DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DOT DOT SPACE DASH DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DASH DASH SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT SPACE DOT DOT DOT DOT SPACE DOT DOT DOT DOT DASH SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DOT SPACE DOT DOT DASH SPACE DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DOT SPACE DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DOT DOT SPACE DASH DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DASH DASH SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT SPACE DASH DOT DOT DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DASH DASH DASH DASH SPACE DASH DOT DOT DOT SPACE DOT DASH DOT SPACE DOT DASH SPACE DASH DOT DASH DOT SPACE DASH DOT DASH SPACE DOT SPACE DASH
We can also verify that the hash is the same as the one obtained after clicking the button:
from Crypto.Hash import SHA256
h = SHA256.new()
h.update(dec)
print(h.hexdigest())
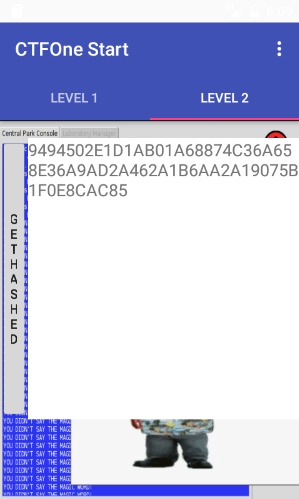
9494502e1d1ab01a68874c36a658e36a9ad2a462a1b6aa2a19075b1f0e8cac85
This seems like morse code, let’s try to decode it.
import morse_talk
morse_code = dec.replace(" ", "").replace("DASH", "-").replace("DOT", ".").replace("SPACE", " ")
print(morse_talk.decode(morse_code))
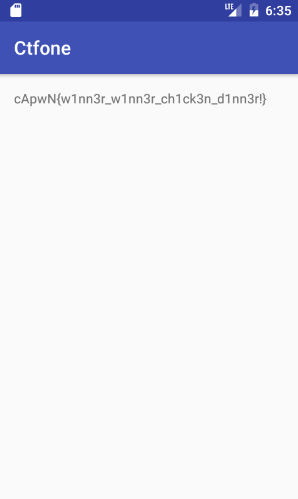
CAPWNBRACKETCRYP706R4PHYUNDERSCORE15UNDERSCOREH4RDUNDERSCOREBR0BRACKET
Replace “BRACKET” and “UNDERSCORE” and there you go!
Level 3
Think you can solve level 3?
While inspecting the decompiled APK, we can find a file named Level3Activity.java. It’s possible to start this activity in adb shell. Make sure you open the app first because the native lib is loaded in the MainActivity class, otherwise it will crash after clicking the button.
➜ adb shell generic:/ $ am start -n com.h1702ctf.ctfone/.Level3Activity Starting: Intent { cmp=com.h1702ctf.ctfone/.Level3Activity }
Great, now we have a button that apparently does nothing. Let’s do some static analysis in order to understand what’s going on.
Level3Activity.java
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Level3Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
class C02211 implements OnClickListener {
class C02201 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
MonteCarlo.start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void onClick(View v) {
new Thread(new C02201()).start();
}
}
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView((int) C0222R.layout.activity_level3);
((Button) findViewById(C0222R.id.button3)).setOnClickListener(new C02211());
}
}
Basically, when we click the button, MonteCarlo.start() is called. While inspecting the MonteCarlo class we can see a declaration of a native function called functionnameLeftbraceOneCommaTwoCommaThreeCommaRightbraceFour. Meanwhile, since this function is never called, I realized that it was probably built for level 4, but I’ll explain it in the next subsection. Let’s continue analyzing the MonteCarlo class.
MonteCarlo.java (click to expand)
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
import android.util.Log;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class MonteCarlo {
private static final String TAG = MonteCarlo.class.toString();
public static class PiValue implements Callable {
double inside = 0.0d;
double pi;
double total = 0.0d;
double f5x;
double f6y;
public Double call() {
for (double i = 0.0d; i < 1000000.0d; i += 1.0d) {
this.f5x = Math.random();
this.f6y = Math.random();
if ((this.f5x * this.f5x) + (this.f6y * this.f6y) <= 1.0d) {
this.inside += 1.0d;
}
this.total += 1.0d;
}
this.pi = (this.inside / this.total) * 4.0d;
return Double.valueOf(this.pi);
}
}
public native String functionnameLeftbraceOneCommaTwoCommaThreeCommaRightbraceFour(String str, String str2, String str3);
public static void start() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ArrayList<Future<Double>> values = new ArrayList();
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
values.add(exec.submit(new PiValue()));
}
ArraysArraysArrays.start();
Double sum = Double.valueOf(0.0d);
Iterator it = values.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
sum = Double.valueOf(sum.doubleValue() + ((Double) ((Future) it.next()).get()).doubleValue());
}
Log.i(TAG, "" + (sum.doubleValue() / ((double) 2)));
Log.i(TAG, "" + ((System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000));
}
}
There’s only one important line of code here for further analysis: ArraysArraysArrays.start().
ArraysArraysArrays.java (click to expand)
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
import android.util.Log;
public class ArraysArraysArrays {
static final /* synthetic */ boolean $assertionsDisabled = (!ArraysArraysArrays.class.desiredAssertionStatus());
private static final String TAG = ArraysArraysArrays.class.toString();
public static native void m9x();
public static void start() {
int[] list = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3};
findAndPrintPairs(list, 5);
bubblesort(list);
showList(list);
list = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11};
bubblesort(list);
showList(list);
list = new int[]{11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2};
bubblesort(list);
showList(list);
m9x();
list = new int[]{1};
bubblesort(list);
showList(list);
}
public static int findMin(int[] list) {
if ($assertionsDisabled || (list != null && list.length > 0)) {
int indexOfMin = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < list.length; i++) {
if (list[i] < list[indexOfMin]) {
indexOfMin = i;
}
}
return indexOfMin;
}
throw new AssertionError("failed precondition");
}
public static void badResize(int[] list, int newSize) {
if ($assertionsDisabled || (list != null && newSize >= 0)) {
int[] temp = new int[newSize];
int limit = Math.min(list.length, newSize);
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
temp[i] = list[i];
}
list = temp;
return;
}
throw new AssertionError("failed precondition");
}
public static int[] goodResize(int[] list, int newSize) {
if ($assertionsDisabled || (list != null && newSize >= 0)) {
int[] result = new int[newSize];
int limit = Math.min(list.length, newSize);
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
result[i] = list[i];
}
return result;
}
throw new AssertionError("failed precondition");
}
public static void findAndPrintPairs(int[] list, int target) {
if ($assertionsDisabled || list != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < list.length; j++) {
if (list[i] + list[j] == target) {
System.out.println("The two elements at indices " + i + " and " + j + " are " + list[i] + " and " + list[j] + " add up to " + target);
}
}
}
return;
}
throw new AssertionError("failed precondition");
}
public static void bubblesort(int[] list) {
if ($assertionsDisabled || list != null) {
boolean changed = true;
for (int i = 0; i < list.length && changed; i++) {
changed = false;
for (int j = 0; j < (list.length - i) - 1; j++) {
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
changed = true;
int temp = list[j + 1];
list[j + 1] = list[j];
list[j] = temp;
}
}
}
if (!$assertionsDisabled && !isAscending(list)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
return;
}
throw new AssertionError("failed precondition");
}
public static void showList(int[] list) {
for (int i : list) {
Log.i(TAG, i + " ");
}
}
public static boolean isAscending(int[] list) {
boolean ascending = true;
int index = 1;
while (ascending && index < list.length) {
if ($assertionsDisabled || (index >= 0 && index < list.length)) {
ascending = list[index + -1] <= list[index];
index++;
} else {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
return ascending;
}
}
There is another native function declaration: m9x. In fact, this function is called inside the start function. We need to understand what this function does… or you can just skip it if you already saw the file Requestor.java.
➜ Reverse Engineering The Native Library
You can find the native library on the directory lib/armeabi-v7a/libnative-lib.so. This is the decompiled code of ArraysArraysArrays.m9x, produced by Hopper Disassembler:
int Java_com_h1702ctf_ctfone_ArraysArraysArrays_x(int arg0) {
sp = sp - 0x18;
r4 = arg0;
if (*(int8_t *)0xc113 == 0x0) {
r0 = 0x0;
do {
*(0xc113 + r0) = *(int8_t *)(0xc05b + r0) ^ 0x3d;
r0 = r0 + 0x1;
} while (r0 != 0x1d);
}
r6 = (*(*r4 + 0x18))(r4, 0xc113, *(*r4 + 0x18));
if (*(int8_t *)0xc131 == 0x0) {
r0 = 0x0;
do {
*(0xc131 + r0) = *(int8_t *)(0xc079 + r0) ^ 0x2c;
r0 = r0 + 0x1;
} while (r0 != 0x7);
}
if (*(int8_t *)0xc139 == 0x0) {
r0 = 0x0;
do {
*(0xc139 + r0) = *(int8_t *)(0xc081 + r0) ^ 0x58;
r0 = r0 + 0x1;
} while (r0 != 0x3);
}
r0 = (*(*r4 + 0x1c4))(r4, r6, 0xc131, 0xc139);
if (r0 != 0x0) {
asm { movne r0, r4 };
}
if (CPU_FLAGS & NE) {
asm { movne r1, r6 };
}
if (CPU_FLAGS & NE) {
r0 = _JNIEnv::CallStaticVoidMethod();
}
return r0;
}
This code can be translated as follows:
bytes_C05B = [0x5E, 0x52, 0x50, 0x12, 0x55, 0xC, 0xA, 0xD, 0xF, 0x5E, 0x49, 0x5B, 0x12, 0x5E, 0x49, 0x5B, 0x52, 0x53, 0x58, 0x12, 0x6F, 0x58, 0x4C, 0x48, 0x58, 0x4E, 0x49, 0x52, 0x4f]
bytes_C079= map(lambda x: ord(x), "^I]YI_X")
bytes_C081 = [0x70, 0x71, 0xE]
bytes_C113 = ""
bytes_C131 = ""
bytes_C139 = ""
for i in range(0x1d):
bytes_C113 += chr(bytes_C05B[i] ^ 0x3d)
for i in range(7):
bytes_C131 += chr(bytes_C079[i] ^ 0x2c)
for i in range(3):
bytes_C139 += chr(bytes_C081[i] ^ 0x58)
#R2 = bytes_C131; R3 = bytes_C139
#BLX R2
#jni_call_method(R6, bytes_C131, bytes_C139)
print("bytes_C113: %s" % bytes_C113)
print("bytes_C131: %s" % bytes_C131)
print("bytes_C139: %s" % bytes_C139)
bytes_C113: com/h1702ctf/ctfone/Requestor bytes_C131: request bytes_C139: ()V
This code basically calls com.h1702ctf.ctfone.Requestor.request() from the native library.
➜ Back to Java 😢
Requestor.java
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
import java.io.IOException;
import okhttp3.CertificatePinner;
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient.Builder;
import okhttp3.Request;
public class Requestor {
private static String sHostname = "h1702ctf.com";
private static String sUrl = "https://h1702ctf.com/About";
public static native String hName();
public static native String hVal();
public static void request() {
try {
new Builder().certificatePinner(new CertificatePinner.Builder().add(sHostname, "sha256/8yKUtMm6FtEse2v0yDMtT0hKagvpKSWHpnufb1JP5g8=").add(sHostname, "sha256/YLh1dUR9y6Kja30RrAn7JKnbQG/uEtLMkBgFF2Fuihg=").add(sHostname, "sha256/Vjs8r4z+80wjNcr1YKepWQboSIRi63WsWXhIMN+eWys=").build()).build().newCall(new Request.Builder().url(sUrl).addHeader(hName(), hVal()).build()).execute();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
Great! More native functions to analyze: hName and hVal. The request function basically requests the URL https://h1702ctf.com/About and sends a header with a given name and value. It’s also important to mention that certeficate pinning is used. I’m going to describe three possible methods to solve this level.
➜ Method 1 - Static Analysis
This is how I originally solved the challenge before trying other methods. I like to do it static if it’s not too complex 😉
I used Hopper Disassembler to decompile functions. Let’s inspect hName and hVal:
void Java_com_h1702ctf_ctfone_Requestor_hName(int arg0) {
r0 = arg0;
if (*(int8_t *)0xc0bc == 0x0) {
r1 = 0x0;
do {
*(0xc0bc + r1) = *(int8_t *)(0xc004 + r1) ^ 0x37;
r1 = r1 + 0x1;
} while (r1 != 0xd);
}
(*(*r0 + 0x29c))();
return;
}
void Java_com_h1702ctf_ctfone_Requestor_hVal(int arg0) {
r0 = arg0;
if (*(int8_t *)0xc0ca == 0x0) {
r1 = 0x0;
do {
*(0xc0ca + r1) = *(int8_t *)(0xc012 + r1) ^ 0x3e;
r1 = r1 + 0x1;
} while (r1 != 0x48);
}
(*(*r0 + 0x29c))();
return;
}
Once again, we can try to replicate the code of these functions.
bytes_C004 = [0x6F, 0x1A, 0x7B, 0x52, 0x41, 0x52, 0x5B, 4, 0x1A, 0x71, 0x5B, 0x56, 0x50]
bytes_C012 = [0x68, 0xF, 0x6C, 0x7D, 0x6C, 0xC, 0x6F, 0x47, 0x6B, 0x66, 0x5A, 0x71, 0x68, 0x79, 0x6C, 0x71, 0x68, 0x53, 0x4E, 0x50, 0x5A, 0xF, 0x52, 0x4D, 0x69, 0x6A, 0x68, 0x55, 0x68, 0xF, 0x74, 0x67, 0x6A, 0x68, 0x5A, 0x4D, 0x6A, 0x55, 0xE, 0x49, 0x5D, 0x79, 0xF, 0x6B, 0x5F, 0x55, 0x4E, 0x48, 0x64, 0x68, 0x6B, 0x46, 0x70, 0x52, 0x6C, 0x4F, 0x5C, 0x7B, 0x6C, 0x5F, 0x5B, 0x54, 0x7F, 0xB, 0x6F, 0xC, 0x5D, 7, 0x6E, 0x6F, 0x51, 3]
hName = ""
hVal = ""
for i in range(0xd):
hName += chr(bytes_C004[i] ^ 0x37)
for i in range(0x48):
hVal += chr(bytes_C012[i] ^ 0x3e)
print("%s: %s" % (hName, hVal))
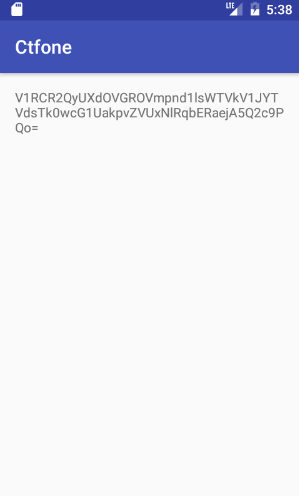
X-Level3-Flag: V1RCR2QyUXdOVGROVmpnd1lsWTVkV1JYTVdsTk0wcG1UakpvZVUxNlRqbERaejA5Q2c9PQo=
Decode the header value as Base64 to get the flag.
➜ Method 2 - An Android Studio Technique
I already described in a previous post a simple method that I’ve been using to reverse native Android stuff. The idea consists in creating a new application in android studio with the same package name. Then, you just need to put the native lib in the directory app/src/main/jniLibs and declare the same native functions inside a class with the same name. I didn’t use Frida to do this task but I heavily suggest you to explore it, it’s really powerful!
Requestor.java (new app)
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class Requestor extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_requestor);
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
tv.setText(hVal());
}
public static native String hName();
public static native String hVal();
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
}
➜ Method 3 - Intercepting The Request
There are some well known methods to intercept HTTPS requests on Android, even if the app uses certificate pinning. The following method also works on non-rooted devices because I’m basically patching the app in order to remove certificate pinning.
I used apktool in order to be able to patch the app.
➜ apktool d ctfone-490954d49dd51911bc730d8161541cf13e7416f9.apk I: Using Apktool 2.1.1 on ctfone-490954d49dd51911bc730d8161541cf13e7416f9.apk I: Loading resource table... I: Decoding AndroidManifest.xml with resources... I: Loading resource table from file: /Users/andrebaptista/Library/apktool/framework/1.apk I: Regular manifest package... I: Decoding file-resources... I: Decoding values */* XMLs... I: Baksmaling classes.dex... I: Copying assets and libs... I: Copying unknown files... I: Copying original files...➜ cd ctfone-490954d49dd51911bc730d8161541cf13e7416f9/smali/com/h1702ctf/ctfone➜ ls ArraysArraysArrays.smali R$anim.smali R$mipmap.smali BuildConfig.smali R$animator.smali R$string.smali InCryption.smali R$attr.smali R$style.smali Level3Activity$1$1.smali R$bool.smali R$styleable.smali Level3Activity$1.smali R$color.smali R.smali Level3Activity.smali R$dimen.smali Requestor.smali MainActivity$1.smali R$drawable.smali TabFragment1$1.smali MainActivity.smali R$id.smali TabFragment1.smali MonteCarlo$PiValue.smali R$integer.smali TabFragment2$1.smali MonteCarlo.smali R$layout.smali TabFragment2.smali PagerAdapter.smali R$menu.smali
Now, we can edit Requestor.smali and patch certificate pinning. The original smail code of request() looks like this:
Requestor.smali (original)
...
.method public static request()V
.locals 11
.prologue
const/4 v10, 0x1
const/4 v9, 0x0
.line 14
new-instance v5, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;
invoke-direct {v5}, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;-><init>()V
sget-object v6, Lcom/h1702ctf/ctfone/Requestor;->sHostname:Ljava/lang/String;
new-array v7, v10, [Ljava/lang/String;
const-string v8, "sha256/8yKUtMm6FtEse2v0yDMtT0hKagvpKSWHpnufb1JP5g8="
aput-object v8, v7, v9
.line 15
invoke-virtual {v5, v6, v7}, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;->add(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/String;)Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;
move-result-object v5
sget-object v6, Lcom/h1702ctf/ctfone/Requestor;->sHostname:Ljava/lang/String;
new-array v7, v10, [Ljava/lang/String;
const-string v8, "sha256/YLh1dUR9y6Kja30RrAn7JKnbQG/uEtLMkBgFF2Fuihg="
aput-object v8, v7, v9
.line 16
invoke-virtual {v5, v6, v7}, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;->add(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/String;)Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;
move-result-object v5
sget-object v6, Lcom/h1702ctf/ctfone/Requestor;->sHostname:Ljava/lang/String;
new-array v7, v10, [Ljava/lang/String;
const-string v8, "sha256/Vjs8r4z+80wjNcr1YKepWQboSIRi63WsWXhIMN+eWys="
aput-object v8, v7, v9
.line 17
invoke-virtual {v5, v6, v7}, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;->add(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/String;)Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;
move-result-object v5
.line 18
invoke-virtual {v5}, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;->build()Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner;
move-result-object v0
...
Multiple certificate hashes are being pinned to h1702ctf.com. It’s easy to bypass this! Just delete the lines between CertificatePinner$Builder;-><init>() and CertificatePinner$Builder;->build().
Requestor.smali (patched)
...
.method public static request()V
.locals 11
.prologue
const/4 v10, 0x1
const/4 v9, 0x0
.line 14
new-instance v5, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;
invoke-direct {v5}, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;-><init>()V
.line 18
invoke-virtual {v5}, Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner$Builder;->build()Lokhttp3/CertificatePinner;
...
➜ apktool b ctfone-490954d49dd51911bc730d8161541cf13e7416f9 -o ctfone-patched.apk
After signing the APK I started my emulator with the -http-proxy option. Then, I installed the patched app and the ~/.mitmproxy/mitmproxy-ca.pem certificate as well. Since we want to capture headers, I wrote a simple mitmproxy script to print them:
def response(flow):
print(flow.request.headers)
➜ mitmdump -s parse_headers.py Loading script: parse_headers.py Proxy server listening at http://0.0.0.0:8080 192.168.1.68:58883: clientconnect Headers[(b'X-Level3-Flag', b'V1RCR2QyUXdOVGROVmpnd1lsWTVkV1JYTVdsTk0wcG1UakpvZVUxNlRqbERaejA5Q2c9PQo='), (b'Host', b'h1702ctf.com'), (b'Connection', b'Keep-Alive'), (b'Accept-Encoding', b'gzip'), (b'User-Agent', b'okhttp/3.8.0')] 192.168.1.68:58883:GET https://138.68.252.172/About <<200 OK 1.44k
Level 4
Hope you kept your notes.
Remember the functionnameLeftbraceOneCommaTwoCommaThreeCommaRightbraceFour declaration in Monte Carlo.java? It’s the only thing left.
int Java_com_h1702ctf_ctfone_MonteCarlo_functionnameLeftbraceOneCommaTwoCommaThreeCommaRightbraceFour(int arg0) {
r7 = (sp - 0x24) + 0xc;
sp = sp - 0x108;
r4 = arg0;
r11 = 0x0;
r10 = (*(*r4 + 0x2a4))(r4, r2, 0x0, *(*r4 + 0x2a4), stack[1982]);
r5 = (*(*r4 + 0x2a4))(r4, r3, 0x0, *(*r4 + 0x2a4));
r6 = (*(*r4 + 0x2a4))(r4, *(r7 + 0x18), 0x0, *(*r4 + 0x2a4), stack[1982]);
strlen(r10);
strlen(r5);
strlen(r6);
asm { strd sb, fp, [sp, #0x108 + var_108] };
asm { strd fp, fp, [sp, #0x108 + var_100] };
crypto_generichash();
asm { strd r8, fp, [sp, #0x108 + var_108] };
asm { strd fp, fp, [sp, #0x108 + var_100] };
crypto_generichash();
asm { strd r0, fp, [sp, #0x108 + var_108] };
asm { strd fp, fp, [sp, #0x108 + var_100] };
r8 = stack[1987];
crypto_generichash();
asm { ldm.w sb, {r0, r2, r3} };
asm { stm r1!, {r0, r2, r3} };
asm { ldm.w r6, {r1, r2, r3} };
asm { stm r0!, {r1, r2, r3} };
asm { ldm r5!, {r0, r2, r3, r6} };
asm { stm r1!, {r0, r2, r3, r6} };
asm { ldm.w r5, {r0, r2, r3, r6} };
r5 = r7 - 0xcd;
asm { stm r1!, {r0, r2, r3, r6} };
crypto_stream_xsalsa20_xor();
*(r7 + 0xffffffffffffff57) = r11;
(*(*r4 + 0x2a8))(r4, stack[1989], r10, *(*r4 + 0x2a8));
(*(*r4 + 0x2a8))(r4, stack[1989], stack[1988], *(*r4 + 0x2a8));
(*(*r4 + 0x2a8))(r4, stack[1989], r8, *(*r4 + 0x2a8));
r0 = (*(*r4 + 0x29c))(r4, r5, *(*r4 + 0x29c));
r1 = **0xbeb8 - stack[2038];
if (r1 == 0x0) {
asm { addeq sp, #0xe4 };
}
if (CPU_FLAGS & E) {
return r0;
}
r0 = __stack_chk_fail();
return r0;
}
It’s not hard to understand that it calls j_crypto_generichash 3 times for each string argument and then uses j_crypto_stream_xsalsa20_xor to decrypt some ciphertext located at 0xA648. There’s nothing more than this. We just need to somehow figure out the correct arguments. Then, I read again the challenge description and the function name: LeftbraceOneCommaTwoCommaThreeCommaRightbrace = (1, 2, 3). I passed the flags of level 1, 2 and 3 to this function using the android studio technique that I described in the previous level and got the flag!
MonteCarlo.java (new app)
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone;
//...
tv.setText(functionnameLeftbraceOneCommaTwoCommaThreeCommaRightbraceFour("cApwN{WELL_THAT_WAS_SUPER_EASY}", "CAPWN{CRYP706R4PHY_15_H4RD_BR0}", "cApwN{1_4m_numb3r_7hr33}"));
//...
public static native String functionnameLeftbraceOneCommaTwoCommaThreeCommaRightbraceFour(String str, String str2, String str3);
Level 5
Hmmm... looks like you need to get past something...
ctfone5-8d51e73cf81c0391575de7b40226f19645777322.apk
Let’s install the app and run it.

I decompiled the APK and found two classes: MainActivity and CruelIntentions.
MainActivity.java (click to expand)
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone5;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton;
import android.support.design.widget.Snackbar;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
class C02201 implements OnClickListener {
C02201() {
}
public void onClick(View view) {
Snackbar.make(view, (CharSequence) "State the secret phrase (omit the oh ex)", 0).setAction((CharSequence) "Action", null).show();
}
}
class C02212 implements OnClickListener {
C02212() {
}
public void onClick(View v) {
((TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(C0222R.id.flagOutput)).setText(
MainActivity.this.flag(((TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(C0222R.id.s0)).getText().toString(),
((TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(C0222R.id.s1)).getText().toString(),
((TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(C0222R.id.s2)).getText().toString()));
((TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(C0222R.id.flagOutput)).setTextColor(-1);
}
}
public native String flag(String str, String str2, String str3);
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView((int) C0222R.layout.activity_main);
setSupportActionBar((Toolbar) findViewById(C0222R.id.toolbar));
((FloatingActionButton) findViewById(C0222R.id.fab)).setOnClickListener(new C02201());
((Button) findViewById(C0222R.id.submitButton)).setOnClickListener(new C02212());
}
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(C0222R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
if (item.getItemId() == C0222R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
CruelIntentions.java (click to expand)
package com.h1702ctf.ctfone5;
import android.app.IntentService;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log;
public class CruelIntentions extends IntentService {
private static final String ACTION_HINT = "com.h1702ctf.ctfone5.action.HINT";
private static final String EXTRA_PARAM1 = "com.h1702ctf.ctfone5.extra.PARAM1";
public native void one();
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
public CruelIntentions() {
super("CruelIntentions");
}
public static void startActionHint(Context context, String param1) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context, CruelIntentions.class);
intent.setAction(ACTION_HINT);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_PARAM1, param1);
context.startService(intent);
}
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
Log.i("BOOYA", "got intent");
if (intent != null) {
if (ACTION_HINT.equals(intent.getAction())) {
Log.i("BOOYA", "got hint");
String param1 = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_PARAM1);
Log.i("BOOYA", "param: " + param1);
handleActionHint(param1);
}
}
}
private boolean rhymesWithOrange(String s) {
return s.equalsIgnoreCase("orange");
}
private void handleActionHint(String param1) {
if (rhymesWithOrange(param1)) {
one();
}
}
}
flag and one are native functions. flag receives three strings and one is a void function. I decided to reverse one statically.
Among other things, this code seems to check if the process is being traced. There is also a call to _system_property_get with the argument 0x291A ➜ 0x293E ➜ 0x2920. In fact, there are some interesting add instructions at 0x2920.
I translated once again the assembly into python:
print(hex(0x5F53D58F+0x5F53D58F))
print(hex(0x7D670F2A+0x7D670F2B))
print(hex(0x6D3D5D2F+0x6D3D5D2F))
print(hex(0x6F56DD5F+0x6F56DD5F))
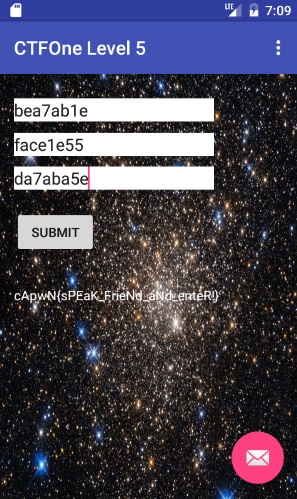
0xbea7ab1e 0xface1e55 0xda7aba5e 0xdeadbabe
With the hint
Level 6
I can't think of anything creative... just try to solve this one :)
ctfone6-6118c10be480b994654a1f01cd322af2df2ceab6.apk
This was my favorite challenge.

I agree, exiting is something useless, that’s what happens when we click the button.
➜ Static Analysis
MainActivity.java (click to expand)
package com.example.asdf;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.pm.Signature;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Debug;
import android.util.Base64;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private static final int BUF_SIZE = 8192;
private static final int INVALID = 1;
private static final String SECONDARY_DEX_NAME = "something.jar";
private static final String SIGNATURE = "4idKtlaGqS2VDhitx2h7UeeEThg=";
private static final int VALID = 0;
private ProgressDialog mProgressDialog = null;
private BroadcastReceiver mReceiver;
private TextView textFuck;
private Button thisShit;
class C00001 implements OnClickListener {
C00001() {
}
public void onClick(View v) {
File dexInternalStoragePath = new File(MainActivity.this.getDir("dex", 0), MainActivity.SECONDARY_DEX_NAME);
new PrepareDexTask().execute(new File[]{dexInternalStoragePath});
}
}
private class PrepareDexTask extends AsyncTask<File, Void, Boolean> {
private PrepareDexTask() {
}
protected void onCancelled() {
super.onCancelled();
if (MainActivity.this.mProgressDialog != null) {
MainActivity.this.mProgressDialog.cancel();
}
}
protected void onPostExecute(Boolean result) {
super.onPostExecute(result);
if (MainActivity.this.mProgressDialog != null) {
MainActivity.this.mProgressDialog.cancel();
}
}
protected Boolean doInBackground(File... dexInternalStoragePaths) {
MainActivity.this.prepareDex(dexInternalStoragePaths[0]);
return null;
}
}
public native void doSomethingCool(Context context);
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(C0001R.layout.main);
if (Debug.isDebuggerConnected()) {
finishAffinity();
System.exit(0);
}
if (checkAppSignature(getApplicationContext()) != 0) {
finishAffinity();
System.exit(0);
}
this.thisShit = (Button) findViewById(C0001R.id.button);
this.textFuck = (TextView) findViewById(C0001R.id.editText);
this.thisShit.setOnClickListener(new C00001());
}
public static boolean isDebuggable(Context context) {
return (context.getApplicationContext().getApplicationInfo().flags & 2) != 0;
}
public int checkAppSignature(Context context) {
try {
for (Signature signature : context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(context.getPackageName(), 64).signatures) {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA");
md.update(signature.toByteArray());<
if (SIGNATURE.trim().equals(Base64.encodeToString(md.digest(), 0).trim())) {
return 0;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
finishAffinity();
System.exit(0);
}
return 1;
}
private boolean prepareDex(File dexInternalStoragePath) {
OutputStream dexWriter;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
OutputStream dexWriter2 = null;
try {
BufferedInputStream bis2 = new BufferedInputStream(getResources().openRawResource(getResources().getIdentifier("something", "raw", getPackageName())));
try {
dexWriter = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dexInternalStoragePath));
} catch (IOException e) {
bis = bis2;
if (dexWriter2 != null) {
try {
dexWriter2.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (bis != null) {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException ioe2) {
ioe2.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[bis2.available()];
bis2.read(buf);
if (!this.textFuck.getText().toString().equals(getResources().getString(C0001R.string.booper))) {
finishAffinity();
System.exit(0);
}
dexWriter.write(decrypt(getResources().getString(C0001R.string.booper), getResources().getString(C0001R.string.dooper), buf));
dexWriter.close();
bis2.close();
try {
System.loadLibrary("idk-really");
doSomethingCool(getApplicationContext());
dexWriter2 = dexWriter;
bis = bis2;
return true;
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e2) {
System.err.println("Native code library failed to load.\n" + e2);
dexWriter2 = dexWriter;
bis = bis2;
return false;
}
} catch (IOException e3) {
dexWriter2 = dexWriter;
bis = bis2;
if (dexWriter2 != null) {
dexWriter2.close();
}
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
return false;
}
} catch (IOException e4) {
if (dexWriter2 != null) {
dexWriter2.close();
}
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
return false;
}
}
public static byte[] decrypt(String key, String initVector, byte[] encrypted) {
try {
IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(initVector.getBytes("UTF-8"));
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes("UTF-8"), "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5PADDING");
cipher.init(2, skeySpec, iv);
return cipher.doFinal(encrypted);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}Well, there are some integrity checks and anti-debugging techniques. The most attractive function is prepareDex. There is also a declaration of a native function named doSomethingCool.
First, it opens two files, one for reading and the other for writing. The file that is being opened is res/raw/something.jar, which is not a valid JAR, just random encrypted data. Our input must match the string resource booper. If it matches, then decrypt is called with the key booper, the IV dooper and the content of res/raw/something.jar. You can find these values and the filename in the files res/values/strings.xml and res/values/raws.xml, respectively, after decoding the resources with apktool.
strings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Level 6</string>
<string name="booper">UCFh%divfMtY3pPD</string>
<string name="diag_message">Processing dex file...</string>
<string name="diag_title">Wait</string>
<string name="dooper">nY6FtpPFXnh,yjvc</string>
<string name="message">Come at me bro</string>
<string name="toast">Toast!</string>
</resources>
raws.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<raw name="secretasset">res/raw/secretasset</raw>
<raw name="something">res/raw/something.jar</raw>
</resources>
So, we have the key and the IV. We can try to decrypt it manually, since we know that it uses AES in ECB mode with PKCS5 padding, or we can just pass the correct key in the EditText and then grab from the emulator the decrypted JAR from the directory /data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex/.
decrypt_something.py
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
pkcs5_unpad = lambda s : s[0:-ord(s[-1])]
f = open("res/raw/something.jar")
ciphertext = f.read()
f.close()
key = "UCFh%divfMtY3pPD"
iv = "nY6FtpPFXnh,yjvc"
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
f = open("decrypted-something.jar", "w")
f.write(pkcs5_unpad(cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)))
f.close()
Good, now let’s extract the decrypted JAR and decompile classes.dex. We have two new java classes:
IReallyHaveNoIdea.java
package com.example.something;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.content.res.Resources;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
public class IReallyHaveNoIdea
{
private BroadcastReceiver mReceiver;
public void getOffMyCase(Context paramContext, String paramString)
{
IntentFilter localIntentFilter = new IntentFilter("com.example.asdf.SEND");
this.mReceiver = new Pooper(new BufferedInputStream(paramContext.getResources().openRawResource(paramContext.getResources().getIdentifier(paramString, "raw", paramContext.getPackageName()))));
paramContext.registerReceiver(this.mReceiver, localIntentFilter);
}
}
Pooper.java (click to expand)
package com.example.something;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class Pooper extends BroadcastReceiver {
private BufferedInputStream bis;
public Pooper(BufferedInputStream _bis) {
this.bis = _bis;
}
public boolean checkSomething1(String a) {
boolean didSomething = true;
int i = 0;
while (i < a.length()) {
switch (a.charAt(i)) {
case '1':
if (i == 1) {
break;
}
didSomething = false;
break;
case '4':
if (!(i == 6 || i == 10)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 'a':
if (i == 2) {
break;
}
didSomething = false;
break;
case 'b':
if (!(i == 0 || i == 4 || i == 8 || i == 12)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 'h':
if (!(i == 3 || i == 7 || i == 11)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 'l':
if (!(i == 5 || i == 9 || i == 13)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 'o':
if (i == 14) {
break;
}
didSomething = false;
break;
case 'p':
if (i == 15) {
break;
}
didSomething = false;
break;
default:
didSomething = false;
break;
}
i++;
}
return didSomething;
}
public boolean checkSomething2(String a) {
boolean didSomething = true;
int i = 0;
while (i < a.length()) {
switch (a.charAt(i)) {
"mmhmthisdatgoods"
case 'a':
if (i == 9) {
break;
}
didSomething = false;
break;
case 'd':
if (!(i == 8 || i == 14)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 'g':
if (i == 11) {
break;
}
didSomething = false;
break;
case 'h':
if (!(i == 2 || i == 5)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 'i':
if (i == 6) {
break;
}
didSomething = false;
break;
case 'm':
if (!(i == 0 || i == 1 || i == 3)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 'o':
if (!(i == 12 || i == 13)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 's':
if (!(i == 7 || i == 15)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
case 't':
if (!(i == 10 || i == 4)) {
didSomething = false;
break;
}
default:
didSomething = false;
break;
}
i++;
}
return didSomething;
}
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String thing1 = intent.getStringExtra("herpaderp");
String thing2 = intent.getStringExtra("lerpaherp");
if (!(checkSomething1(thing1) && checkSomething2(thing2))) {
System.exit(0);
}
File soInternalStoragePath = new File(context.getDir("dex", 0), "super-dooper");
soInternalStoragePath.delete();
try {
BufferedOutputStream soWriter = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(soInternalStoragePath));
byte[] buf = new byte[this.bis.available()];
this.bis.read(buf);
soWriter.write(decrypt(thing1, thing2, buf));
soWriter.close();
this.bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
soInternalStoragePath.setExecutable(true);
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(soInternalStoragePath.getAbsolutePath());
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
public static byte[] decrypt(String key, String initVector, byte[] encrypted) {
try {
IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(initVector.getBytes("UTF-8"));
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes("UTF-8"), "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5PADDING");
cipher.init(2, skeySpec, iv);
return cipher.doFinal(encrypted);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}I also reversed the native function doSometingCool and realized that it was calling com.example.something.IReallyHaveNoIdea.getOffMyCase() with the paramString 0x1B230 to 0x1B23B with 0x3e.
The getOffMyCase function basically registers the BroadcastReceiver and initializes Pooper which extends BroadcastReceiver. When Pooper receives a broadcast intent it calls checkSomething1 and checkSomething2. From these functions it’s easy to get the key and the IV of the next decrypt call.
decrypt_secretasset.py
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
pkcs5_unpad = lambda s : s[0:-ord(s[-1])]
f = open("res/raw/secretasset")
ciphertext = f.read()
f.close()
key = "b1ahbl4hbl4hblop"
iv = "mmhmthisdatgoods"
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
f = open("super-dooper", "w")
f.write(pkcs5_unpad(cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)))
f.close()
Then, the decrypted secret asset is executed by Runtime.getRuntime().exec().
➜ file super-dooper super-dooper: ELF 32-bit LSB shared object, ARM, EABI5 version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /system/bin/linker, BuildID[sha1]=12c1ab8273eb1b3b193b61aaa45a2a02a332f32f, stripped
I executed super-dooper but it apparently did nothing.
➜ adb shell generic:/ $ su generic:/ # cd /data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex/ generic:/data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex # ./super-dooper
➜ More Static Analysis (native)
Let’s reverse super-dooper. I found the reason why the binary was “doing nothing”. It’s a server.
int sub_2690() {
sp = sp - 0x68;
stack[2037] = **0x5f54;
r0 = socket(0x2, 0x1, 0x0);
r8 = r0;
if ((bind(r0, sp + 0x1c, 0x10) < 0x0) || (listen(r8, 0xa) < 0x0)) goto loc_27a2;
loc_26d6:
r5 = sp + 0x2c;
r9 = sp + 0x18;
stack[2023] = 0x6ec8;
stack[2022] = sp + 0x14;
goto loc_2700;
loc_2700:
do {
r0 = accept(r8, r5, r9);
r11 = r0;
if (*0x6cbc != 0x63) {
break;
}
close(r0);
} while (true);
r7 = 0x6000;
r0 = malloc(0x38);
lr = *(r7 + 0xaf4);
r12 = *(int8_t *)0x6ec8;
r4 = r0;
asm { ldm.w r5, {r0, r1, r2, r3} };
*(r4 + 0x10) = r11;
*(r4 + 0x14) = lr;
asm { stm.w r4, {r0, r1, r2, r3} };
r0 = r4 + 0x18;
*(r7 + 0xaf4) = lr + 0x1;
if (r12 == 0x0) {
*0x6ec8 = *(int8_t *)0x6af8 ^ 0x5e;
*0x6ec9 = *(int8_t *)0x6af9 ^ 0x5e;
}
sprintf(r0, stack[2023]);
r2 = 0x6afc;
r3 = 0x0;
goto loc_2760;
loc_2760:
r2 = r2 + 0x4;
if (*r2 != 0x0) goto loc_275a;
loc_2768:
*(0x6b00 + r3 * 0x2) = r4;
goto loc_276e;
loc_276e:
pthread_create(stack[2022], 0x0, 0x1b11, r4);
sleep(0x1);
goto loc_2700;
loc_275a:
r3 = r3 + 0x1;
if (r3 == 0x64) goto loc_276e;
goto loc_2760;
loc_27a2:
r0 = 0x1;
if (stack[2037] != **0x5f54) {
r0 = __stack_chk_fail();
}
return r0;
}
In sub_2690 the program calls socket, bind, listen and accept. Then it creates a thread for each client with the handler function sub_1B10. I uncovered the server port using netstat.
generic:/data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex # netstat -l Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1337 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
sub_1B10-decompiled.c (click to expand)
int sub_1b14(int arg0) {
r0 = arg0;
sp = sp - 0x24;
asm { subw sp, sp, #0x874 };
r9 = r0;
stack[2040] = *(r3 + 0x1b26);
stack[2578] = **(r3 + 0x1b26);
*0x6cbc = *0x6cbc + 0x1;
if (*(int8_t *)(0x6b00 + "3816874") == 0x0) {
r6 = *0x68ec ^ 0x33333333;
r5 = *0x68f0 ^ 0x33333333;
r4 = *0x68f4 ^ 0x33333333;
r0 = *0x68f8 ^ 0x33333333;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x68fc ^ 0x33;
*(0x6b00 + "3816874") = r6;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x68fd ^ 0x33;
*0x6cc4 = r5;
*0x6cc8 = r4;
*0x6ccc = r0;
*0x6cd0 = r1;
*0x6cd1 = r2;
}
r4 = sp + 0x6c;
stack[2039] = r9 + 0x18;
r10 = 0x6afc;
r6 = r10;
sprintf(r4, 0x6b00 + "3816874");
do {
r6 = r6 + 0x4;
r7 = *r6;
if (r7 != 0x0) {
write(*(r7 + 0x10), r4, strlen(r4));
}
} while (r6 != 0x6c8c);
r3 = 0x4f6c;
asm { addw fp, sp, #0x46c };
stack[2042] = r3 + 0x1e58;
goto loc_1ba4;
loc_1ba4:
r0 = read(*(r9 + 0x10), r11, 0x3ff);
if (r0 <= 0x0) goto loc_1c32;
loc_1bb6:
*(r11 + r0) = 0x0;
r3 = *(int8_t *)r11;
*r4 = 0x0;
if (r3 == 0x0) goto loc_1ba4;
loc_1bc4:
r2 = r11;
do {
if (r3 != 0xd) {
asm { cmpne r3, #0xa };
}
if (CPU_FLAGS & E) {
asm { strbeq r6, [r2] };
}
r2 = r2 + 0x1;
r3 = *(int8_t *)r2;
} while (r3 != 0x0);
r3 = *(int8_t *)r11;
if (r3 == 0x0) goto loc_1ba4;
loc_1be0:
if (r3 == 0x5c) goto loc_1d14;
loc_1be6:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6ebc == 0x0) {
*0x6ebd = *(int8_t *)0x6ad5 ^ 0x35;
*0x6ebe = *(int8_t *)0x6ad6 ^ 0x35;
*0x6ebf = *(int8_t *)0x6ad7 ^ 0x35;
r0 = *(int8_t *)0x6ad8 ^ 0x35;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x6ad9 ^ 0x35;
*0x6ec0 = r0;
*0x6ec1 = r1;
r6 = *(int8_t *)0x6ad4 ^ 0x35;
r0 = *(int8_t *)0x6ada ^ 0x35;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x6adb ^ 0x35;
*0x6ebc = r6;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x6adc ^ 0x35;
*0x6ec2 = r0;
*0x6ec3 = r1;
*0x6ec4 = r2;
}
r7 = r10;
sprintf(r4, 0x6ebc);
r8 = *(r9 + 0x14);
do {
r7 = r7 + 0x4;
r6 = *r7;
if ((r6 != 0x0) && (r8 != *(r6 + 0x14))) {
write(*(r6 + 0x10), r4, strlen(r4));
}
} while (0x6c8c != r7);
goto loc_1ba4;
loc_1d14:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6cd4 == 0x0) {
*0x6cd4 = *(int8_t *)0x6900 ^ 0x28;
}
r7 = strtok(r11, 0x6cd4);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6cd8 == 0x0) {
*0x6cd9 = *(int8_t *)0x6905 ^ 0x5a;
r0 = *(int8_t *)0x6904 ^ 0x5a;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x6906 ^ 0x5a;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x6907 ^ 0x5a;
*0x6cd8 = r0;
r3 = *(int8_t *)0x6908 ^ 0x5a;
*0x6cda = r1;
*0x6cdb = r2;
*0x6cdc = r3;
}
if (strcmp(r7, 0x6cd8) == 0x0) goto loc_1c32;
loc_1d56:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6cf4 == 0x0) {
*0x6cf5 = *(int8_t *)0x690d ^ 0x60;
r0 = *(int8_t *)0x690c ^ 0x60;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x690e ^ 0x60;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x690f ^ 0x60;
*0x6cf4 = r0;
r3 = *(int8_t *)0x6910 ^ 0x60;
*0x6cf6 = r1;
*0x6cf7 = r2;
*0x6cf8 = r3;
}
if (strcmp(r7, 0x6cf4) == 0x0) goto loc_1edc;
loc_1d76:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d08 == 0x0) {
*0x6d09 = *(int8_t *)0x6921 ^ 0x55;
r0 = *(int8_t *)0x6920 ^ 0x55;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x6922 ^ 0x55;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x6923 ^ 0x55;
*0x6d08 = r0;
r3 = *(int8_t *)0x6924 ^ 0x55;
*0x6d0a = r1;
*0x6d0b = r2;
*0x6d0c = r3;
}
if (strcmp(r7, 0x6d08) != 0x0) goto loc_1f04;
loc_1d96:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d10 == 0x0) {
*0x6d10 = *(int8_t *)0x6928 ^ 0x54;
}
r0 = strtok(0x0, 0x6d10);
r8 = r0;
if (r0 == 0x0) goto loc_2380;
loc_1dc6:
r7 = strdup(stack[2039]);
strcpy(stack[2039], r8);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d14 == 0x0) {
*0x6d18 = *0x6930 ^ 0x57575757;
r2 = *0x6934 ^ 0x57575757;
r1 = *0x692c ^ 0x57575757;
r3 = *0x6938 ^ 0x57575757;
*0x6d14 = r1;
r0 = *0x693c ^ 0x57575757;
*0x6d1c = r2;
*0x6d20 = r3;
*0x6d24 = r0;
}
r6 = r10;
sprintf(r4, 0x6d14);
free(r7);
do {
r6 = r6 + 0x4;
r7 = *r6;
if (r7 != 0x0) {
write(*(r7 + 0x10), r4, strlen(r4));
}
} while (0x6c8c != r6);
goto loc_1ba4;
loc_2380:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d2c == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6d2c;
r3 = 0x17;
r0 = 0x48;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x944 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
r6 = 0x6d2c;
goto loc_1ef0;
loc_1ef0:
write(*(r9 + 0x10), r6, strlen(r6));
goto loc_1ba4;
loc_1f04:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d44 == 0x0) {
*0x6d45 = *(int8_t *)0x695d ^ 0x60;
*0x6d46 = *(int8_t *)0x695e ^ 0x60;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x695f ^ 0x60;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x6960 ^ 0x60;
*0x6d47 = r1;
*0x6d48 = r2;
r0 = *(int8_t *)0x695c ^ 0x60;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x6961 ^ 0x60;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x6962 ^ 0x60;
*0x6d44 = r0;
r3 = *(int8_t *)0x6963 ^ 0x60;
*0x6d49 = r1;
*0x6d4a = r2;
*0x6d4b = r3;
}
if (strcmp(r7, 0x6d44) == 0x0) {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d50 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6d50;
r3 = 0x1;
r0 = 0x5e;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x968 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
r0 = strtok(0x0, 0x6d50);
if (r0 != 0x0) {
stack[2044] = atoi(r0);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d54 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6d54;
r3 = 0x1;
r0 = 0x32;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x96c };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
r0 = strtok(0x0, 0x6d54);
r6 = r0;
if (r0 != 0x0) {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d58 == 0x0) {
sub_174c(0x3b, 0x6970, 0x6d58, 0x8);
}
r8 = 0x6b00;
sprintf(r4, 0x6d58);
stack[2047] = 0x6b00;
stack[2048] = 0x6d68;
do {
if (*(int8_t *)(r8 + 0x264) == 0x0) {
*(r8 + 0x264) = *(int8_t *)0x697c ^ 0x1e;
}
strcat(r4, 0x6d64);
strcat(r4, r6);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d68 == 0x0) {
*0x6d68 = *(int8_t *)0x6980 ^ 0x44;
}
r0 = strtok(0x0, stack[2048]);
r6 = r0;
if (r0 == 0x0) {
break;
}
else {
continue;
}
} while (true);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d6c == 0x0) {
r0 = 0x27;
r1 = 0x6000;
r2 = stack[2047] + 0x26c;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x984 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, 0x2);
}
strcat(r4, 0x6d6c);
sub_1820(r4, stack[2044], *(r9 + 0x10));
}
else {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d70 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6d70;
r0 = 0x36;
r3 = 0x1a;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x988 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
sub_1808(0x6d70, *(r9 + 0x10));
}
}
else {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6d8c == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6d8c;
r0 = 0x29;
r3 = 0x1c;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x9a4 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
sub_1808(0x6d8c, *(r9 + 0x10));
}
}
else {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6dac == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6dac;
r3 = 0x7;
r0 = 0x27;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x9c4 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
if (strcmp(r7, 0x6dac) == 0x0) {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6db4 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6db4;
r3 = 0xe;
r0 = 0x4c;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x9cc };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
r6 = r10;
r7 = sp + 0x2c;
sprintf(r4, 0x6db4);
write(*(r9 + 0x10), r4, strlen(r4));
stack[2045] = r10;
stack[2046] = r9;
stack[2047] = r4;
r8 = *(r9 + 0x10);
r4 = 0x6000;
r10 = stack[2042];
do {
r6 = r6 + 0x4;
r3 = *r6;
if (r3 != 0x0) {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6dc4 == 0x0) {
*0x6dc8 = *(r4 + 0x9e0) ^ 0x3a3a3a3a;
r1 = *(r4 + 0x9e4) ^ 0x3a3a3a3a;
r2 = *(r4 + pthread_detach) ^ 0x3a3a3a3a;
*0x6dcc = r1;
*0x6dd0 = r2;
r0 = *(r4 + pthread_self) ^ 0x3a3a3a3a;
r1 = *(int8_t *)(r4 + 0x9ec) ^ 0x3a;
*0x6dc4 = r0;
r2 = *(int8_t *)(r4 + 0x9ed) ^ 0x3a;
*0x6dd4 = r1;
*0x6dd5 = r2;
}
sprintf(r7, r10);
write(r8, r7, strlen(r7));
}
if (0x6c8c == r6) {
break;
}
else {
continue;
}
} while (true);
r10 = stack[2045];
r9 = stack[2046];
r4 = stack[2047];
}
else {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6dd8 == 0x0) {
sub_174c(0x2e, "rfkb~", 0x6dd8, 0x5);
}
if (strcmp(r7, 0x6dd8) == 0x0) {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6de0 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6de0;
r0 = 0x52;
r3 = 0x19;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0x9f8 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
strcat(r4, 0x6de0);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6dfc == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6dfc;
r0 = 0x2c;
r3 = 0x17;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0xa14 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
strcat(r4, 0x6dfc);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6e14 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6e14;
r0 = 0x28;
r3 = 0x22;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0xa2c };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
strcat(r4, 0x6e14);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6e38 == 0x0) {
sub_174c(0x42, 0x6a50, 0x6e38, 0x36);
}
strcat(r4, 0x6e38);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6e70 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6e70;
r0 = 0x60;
r3 = 0x1f;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0xa88 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
strcat(r4, 0x6e70);
if (*(int8_t *)0x6e90 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x6e90;
r0 = 0x2d;
r3 = 0x15;
r1 = 0x6000;
asm { addw r1, r1, #0xaa8 };
sub_174c(r0, r1, r2, r3);
}
strcat(r4, 0x6e90);
sub_1808(r4, *(r9 + 0x10));
}
else {
if (*(int8_t *)0x6ea8 == 0x0) {
sub_174c(0x22, 0x6ac0, 0x6ea8, 0x12);
}
sub_1808(0x6ea8, *(r9 + 0x10));
}
}
}
goto loc_1ba4;
loc_1edc:
if (*(int8_t *)0x6cfc == 0x0) {
*0x6cfd = *(int8_t *)0x6915 ^ 0x21;
*0x6cfe = *(int8_t *)"qnof,+" ^ 0x21;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x6917 ^ 0x21;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x6918 ^ 0x21;
*0x6cff = r1;
*0x6d00 = r2;
r0 = *(int8_t *)0x6914 ^ 0x21;
r1 = *(int8_t *)0x6919 ^ 0x21;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x691a ^ 0x21;
*0x6cfc = r0;
r3 = *(int8_t *)0x691b ^ 0x21;
*0x6d01 = r1;
*0x6d02 = r2;
*0x6d03 = r3;
}
r6 = 0x6cfc;
goto loc_1ef0;
loc_1c32:
close(*(r9 + 0x10));
if (*(int8_t *)0x6ce0 == 0x0) {
r6 = *0x6ae0 ^ 0x27272727;
r0 = *0x6ae4 ^ 0x27272727;
r7 = *0x6ae8 ^ 0x27272727;
r1 = *0x6aec ^ 0x27272727;
*0x6ce0 = r6;
r2 = *(int8_t *)0x6af0 ^ 0x27;
*0x6ce4 = r0;
*0x6ce8 = r7;
*0x6cec = r1;
*0x6cf0 = r2;
}
r6 = r10;
sprintf(r4, 0x6ce0);
do {
r6 = r6 + 0x4;
r7 = *r6;
if (r7 != 0x0) {
write(*(r7 + 0x10), r4, strlen(r4));
}
} while (r6 != 0x6c8c);
r1 = *(r9 + 0x14);
r3 = 0x0;
goto loc_1cc4;
loc_1cc4:
r10 = r10 + 0x4;
r2 = *r10;
if ((r2 == 0x0) || (r1 != *(r2 + 0x14))) goto loc_1cbe;
loc_1cd2:
*(0x6b00 + r3 * 0x2) = 0x0;
goto loc_1cde;
loc_1cde:
free(r9);
*0x6cbc = *0x6cbc - 0x1;
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
r0 = 0x0;
if (stack[2578] == *stack[2040]) {
asm { addw sp, sp, #0x874 };
}
else {
r0 = __stack_chk_fail();
}
return r0;
loc_1cbe:
r3 = r3 + 0x1;
if (r3 == 0x64) goto loc_1cde;
}
The handler function is big! However, we can notice that some things are being XORed. For example at the address 0x1E2A, dword_68EC is XORed with 0x33333333. In this case, the result is the string
\QUIT➜ Disconnect\PING➜ Receive “«PONG” from the server\NAME new_name➜ Change username\PRIVATE dest_user_id some private message➜ Send a private message to a given user
If no command is used the input is sent to all users. Then, I found some suspicious code on the function that handles the \PRIVATE command: sub_1820.
I tried to understand what this function was doing. After some time analyzing it, I wrote the following pseudocode:
#arguments
msg = "... gettin it done ..."
dest_user_id = 1337
dword_6C90 = "gettin it done"
n = len(dword_6C90)
#.text:0000185E CMP R11, R7
if dest_id == 0x539: #1337
dword_6CA0 = "gettin it done"
index = msg.find(" ")+1 #strchr 32
if msg[index:n] == dword_6CA0: #strncmp
#.text:000018CA ADD.W R2, R10, #2
msg_b = msg[n+2:] #msg_b = "..."
s_msg_b = do some sorcery with msg_b #sub_15A0, sub_15D8, sub_1668
for i in range(???):
if dword_6020[i] == s_msg_b[i] #and more conditions?
send back "Nice one!" to client
send message to destination
So, our private message must start with msg_b). I decided not to go any further than this using static analysis because the sorcery functions are hard to understand. I’m going to debug the process in order to understand what’s happening and what is being compared.
➜ Dynamic Analysis
generic:/data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex # ps | grep super-dooper root 26682 11384 4496 984 inet_csk_a afe4e1c0 S ./super-dooper generic:/data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex # gdbserver :8888 --attach 26682 Attached; pid = 26682 Listening on port 8888
➜ adb forward tcp:8888 tcp:8888➜ ./gdb(gdb) target remote:8888 0xafe4e1bc in __accept4 () from target:/system/lib/libc.so(gdb) info proc map process 26682 Mapped address spaces: Start Addr End Addr Size Offset objfile 0xafaf2000 0xafaf3000 0x1000 0x0 [anon:thread stack guard page] ... 0xaff71000 0xaff75000 0x4000 0x0 /data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex/super-dooper 0xaff76000 0xaff77000 0x1000 0x4000 /data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex/super-dooper 0xaff77000 0xaff78000 0x1000 0x5000 /data/data/com.example.asdf/app_dex/super-dooper 0xbe83d000 0xbe85e000 0x21000 0x0 [stack] 0xffff0000 0xffff1000 0x1000 0x0 [vectors]
The .text base address is 0xaff71000. We need this address to calculate breakpoints in order to inspect certain states of execution, because addresses are randomized due to ASLR (PIE). It’s also important to keep threading in mind. I connected from new client and switched to the client thread. Then I set a breakpoint at 0x1820.
(gdb) i threads Id Target Id Frame * 1 Thread 26682.26682 "super-dooper" 0xafe4e1bc in __accept4 () from target:/system/lib/libc.so 3 Thread 26682.17763 "super-dooper" 0xafe4f3f0 in read () from target:/system/lib/libc.so(gdb) thread 3 [Switching to thread 3 (Thread 26682.17763)] #0 0xafe4f3f0 in read () from target:/system/lib/libc.so(gdb) b *0xaff72820 Breakpoint 1 at 0xaff72820(gdb) c Continuing.
I decided to send a flag starting with
➜ nc 127.0.0.1 1337 <<JOIN, HELLO 13 \PRIVATE 1337 gettin it done cApABABABABABA
Suddenly…
Thread 3 "super-dooper" received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault. 0xafe1f150 in strlen () from target:/system/lib/libc.so
I didn’t understand why it crashes, maybe due to some anti-debugging protection causing it to segfault… No problem, we can jump to sub_2820 with the correct arguments.
(gdb) i r r0 0x0 0 r1 0x539 1337 r2 0x80808080 2155905152 r3 0x3 3 r4 0x0 0 r5 0x539 1337 r6 0x0 0 r7 0xaff77b00 2952231680 r8 0xaff77b00 2952231680 r9 0xafca00a8 2949251240 r10 0xaff77afc 2952231676 r11 0xafbf04e4 2948531428 r12 0x0 0 sp 0xafbf0068 0xafbf0068 lr 0xaff72813 -1342756845 pc 0xafe1f150 0xafe1f150 <strlen+48> cpsr 0x40000030 1073741872(gdb) x/3x $sp 0xafbf0068: 0x00000003 0xafbf00e4 0xaff77c8c(gdb) x/s 0xafbf00e4 0xafbf00e4: "[PM][13] gettin it done cApABABABABABA\r\n"(gdb) set $r0=0xafbf00e4(gdb) set $r2=0x539(gdb) j *0xaff72820 Continuing at 0xaff72820. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 1, 0xaff72820 in ?? ()
Now, we can debug from this point and set new breakpoints. I decided to set a breakpoint at the first comparison, after the execution of the “sorcery” functions (sub_15A0, sub_15D8 and sub_1668).
(gdb) x/i 0xaff7293a 0xaff7293a: cmp r1, r2(gdb) b *0xaff7293a Breakpoint 4 at 0xaff7293a(gdb) c Continuing. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 4, 0xaff7293a in ?? ()(gdb) i r r0 0xafbeff94 2948530068 r1 0xfc 252 r2 0xfc 252 ...(gdb) c Continuing. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 4, 0xaff7293a in ?? ()(gdb) i r r0 0xafbeff94 2948530068 r1 0xe2 226 r2 0xe2 226 ...(gdb) c Continuing. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 4, 0xaff7293a in ?? ()(gdb) i r r0 0xafbeff94 2948530068 r1 0x2d 45 r2 0x2d 45 ...(gdb) c Continuing. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 4, 0xaff7293a in ?? ()(gdb) i r r0 0xafbeff94 2948530068 r1 0x55 85 r2 0xe2 226 ...
Nice! This means that our first three characters are correct, but the 4th is wrong, which makes sense.
(gdb) c Continuing. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 4, 0xaff7293a in ?? ()(gdb) i r r0 0xafbeff94 2948530068 r1 0x79 121 r2 0x83 131 ...(gdb) c Continuing. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 4, 0xaff7293a in ?? ()(gdb) i r r0 0xafbeff94 2948530068 r1 0x56 86 r2 0xe2 226 ...(gdb) c Continuing. Thread 3 "super-dooper" hit Breakpoint 4, 0xaff7293a in ?? ()(gdb) i r r0 0xafbeff94 2948530068 r1 0x11 17 r2 0x83 131 ...
My flag was R2. Did you see the pattern? 'A' = 0xe2 and 'B' = 0x83! Some character mapping is happening here and R1 holds the correct values.
I continued to debug like this and found the correct character mapping and the correct flag values.
char_values = {0xc7: "a", 0xf7: "b", 0xfc: "c", 0x11: "d", 0x1b: "e", 0x33: "f", 0xe7: "g", 0xef: "h", 0xca: "i", 0x6b: "j", 0x21: "k", 0x01: "l", 0x33: "m", 0xfe: "n", 0x0c: "o", 0x2d: "p", 0xaf: "q", 0xe2: "r", 0xea: "s", 0xcc: "t", 0xf3: "u", 0x79: "v", 0x55: "w", 0x0f: "x", 0xcb: "y", 0x8c: "z", 0xb3: "0", 0xa9: "1", 0x88: "2", 0x35: "3", 0x70: "4", 0x83: "5", 0x6d: "6", 0x63: "7", 0x3e: "8", 0xce: "9", 0xe2: "A", 0x83: "B", 0x95: "C", 0x65: "D", 0xac: "_", 0xad: "}"}
flag = [0xfc, 0xe2, 0x2d, 0x55, 0x79, 0x56, 0x11, 0x35, 0xf3, 0xea, 0xac, 0x11, 0x35, 0x0f, 0xac, 0x33, 0xcb, 0xac, 0x70, 0x2d, 0x21, 0xac, 0xca, 0xea, 0xac, 0xc7, 0xf3, 0xe7, 0x33, 0x35, 0xfe, 0xcc, 0x1b, 0x11, 0xad]
iOS Writeups
These challenges were compiled for real devices. iOS Simulator is not an option because it can’t run armv7 or arm64 apps. I don’t have an iPhone and it took me a few days to get one from my University. Many thanks to professor Luís Antunes and Luís Maia.
Note: Levels 1-4 were originally solved statically because I still didn’t have the iPhone. I decided to reverse armv7.
Level 1
WAKE ME UP, WAKE ME UP INSIDE. SAVE ME!!!!!
(Note: Levels 1-4 use the same application)
IntroLevels-727e07e27199b5431fccc16850d67c4fea6596f7.ipa
There’s nothing in the screen, only a image. Is this level similar to android level 1? Where are the assets in iOS apps? I extracted the IPA file and found Assets.car. I used AssetCatalogTinkerer to view the assets and got the flag.

Level 2
And he prays...
Hopper Disassembler is really good for reversing iOS apps. I loaded the binary IntroLevels in Hopper and found the function [IntroLevels.Level2ViewController buttonTouched:] at 0xB020. I inspected the procedure at 0xA930, which is called by the previous function, and realized that it was calculating the MD5 hash of a given input and comparing it to the hexdigest 0xAC8C some values are stored in some sort of array. Let’s try to use them as the ciphertext.
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
key = "4242411234424241"
iv = "deadbeefc4febab3"
l = [0xd3, 0x33, 0x6b, 0x68, 0x29, 0xf6, 0x72, 0x67, 0xe, 0x80, 0x21, 0x3, 0x3a, 0x73] #mov instructions
l += [0x1c, 0x94, 0x0f, 0x31, 0x28, 0xab, 0x40, 0x63, 0x4e, 0x29, 0x11, 0xb9, 0xf1, 0xf4, 0x3f, 0x92] #{d16, d17}: 0xB010
l += [0xd4, 0xa6] #movw r1, #0xa6d4
enc = "".join(map((lambda n: chr(n)), l))
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
print(cipher.decrypt(enc))
It was so much easier if I had a device at the time…
Level 3
Rock, paper, scissors is so juvenile. Play rock, paper, scissors, lizard, Spock!

This one was not easy to solve statically. We were supposed to sniff an HTTPS connection instead, just like I did on android level 3 (method 3).
So, I started analyzing the assembly code of Level 3, especially sub_D828, which is called by [IntroLevels.Level3ViewController viewDidLoad] at 0xECBC.
int sub_d828(int arg0) {
...
sub_3a918(r7 - 0x30, "l", 0x1, 0x0, r8, r6, r4, r0);
if (var_24 == 0x0) {
swift_unknownRelease(var_28);
}
...
sub_3a918(r7 - 0x30, "c" , r2, 0x0, stack[2018], r5, r4, stack[2022]);
if (var_24 == 0x0) {
swift_unknownRelease(var_28);
}
sub_ece0(r11);
sub_1cfe4(r11);
sub_1e460(r11);
sub_1f8dc(r11);
sub_ece0(r11);
sub_10180(r11);
sub_168a0(r11);
sub_15400(r11);
sub_11620(r11);
sub_168a0(r11);
sub_20d58(r11);
sub_221d4(r11);
sub_25f48(r11);
sub_23650(r11);
sub_24acc(r11);
sub_12ac0(r11);
sub_19204(r11);
sub_168a0(r11);
sub_25f48(r11);
sub_28840(r11);
sub_24acc(r11);
sub_273c4(r11);
sub_2c5b4(r11);
sub_24acc(r11);
sub_28840(r11);
sub_29cbc(r11);
sub_29cbc(r11);
sub_2da30(r11);
sub_13f60(r11);
sub_168a0(r11);
sub_15400(r11);
sub_12ac0(r11);
sub_1f8dc(r11);
sub_2b138(r11);
sub_2c5b4(r11);
sub_3409c(r11);
sub_24acc(r11);
sub_2da30(r11);
sub_168a0(r11);
sub_15400(r11);
sub_2eeac(r11);
sub_2c5b4(r11);
sub_2eeac(r11);
sub_168a0(r11);
sub_17d40(r11);
sub_19204(r11);
sub_15400(r11);
sub_1a6a4(r11);
sub_19204(r11);
sub_30328(r11);
sub_317a4(r11);
sub_32c20(r11);
sub_3409c(r11);
sub_35518(r11);
sub_1bb44(r11);
if (*0x459cc == 0x0) {
if (*0x459d0 == 0x0) {
r2 = 0x0;
r0 = swift_getTupleTypeMetadata2();
r1 = 0x36e58;
asm { dmb };
*(0xeb78 + r1) = r0;
}
r0 = type metadata accessor for Swift._ContiguousArrayStorage();
r1 = 0x36e3c;
asm { dmb };
*(0xeb90 + r1) = r0;
}
r3 = 0x0;
r6 = swift_initStackObject();
r0 = 0x33766;
asm { vmov.i32 d1, #0x2 };
r0 = 0xebb0 + r0;
asm { vmov.i32 d2, #0x1 };
asm { vmov.i32 d0, #0xc };
r8 = 0x0;
r0 < 0x10 | r0;
asm { vmov.f32 s5, s2 };
asm { vmov.f32 s7, s0 };
asm { vst1.32 {d2, d3}, [r0] };
*(r6 + 0x1c) = r8;
r7 = r7;
[[sub_ba14() mainBundle] retain];
*(r6 + 0x20) = static Alamofire.ServerTrustPolicy.certificates ();
...
}
sub_3a918 is called with the string sub_3A918 in the whole binary. Then, there are lots of calls to different functions, all very similar. There are some visible differences between them in terms of characters, including the character passed as argument to sub_3a918.
int sub_ece0(int arg0) {
...
if ((r4 & (0xc0000000 ^ 0xffffffff)) != 0x0) {
var_20 = r6;
swift_unknownRetain(r6);
function signature specialization <preserving fragile attribute, Arg[0] = Owned To Guaranteed and Exploded> of Swift._StringCore.append ();
r8 = r5;
r4 = r4;
r5 = var_20;
}
else {
r5 = 0x0;
r4 = 0x1;
r8 = "o"
}
swift_unknownRelease(r6);
sub_3a918(r7 - 0x28, r8, r4, r5, stack[2030], stack[2029], stack[2028], r10);
goto loc_10034;
loc_10034:
r0 = var_1C;
if (r0 == 0x0) {
r0 = swift_unknownRelease(var_20);
}
return r0;
...
}
So, the next character is
lcoApwok at N{1m_me 1n_ur_n00ti amwork_t aere heade3fik}r
This looks like a flag! I separated a clear sentence from the flag:
I sniffed the HTTPS connection later when I got my device by replacing google.cer with the certificate of my proxy and adding the proxy in WiFi settings.
Level 4
Use your flags from levels 1, 2, and 3 to do the thing!

Ok, let’s do the thing. This is the decompiled code produced by Hopper Disassembler for the procedure [ZhuLi doTheThing:flag2:flag3:] at 0xA0D8:
doTheThing-decompiled.c (click to expand)
void * +[ZhuLi doTheThing:flag2:flag3:](void * self, void * _cmd, void * arg2, void * arg3, void * arg4) {
r3 = arg3;
r2 = arg2;
r7 = (sp - 0x14) + 0xc;
r4 = sp - 0xc0;
asm { bfc r4, #0x0, #0x3 };
sp = r4;
r6 = [r2 retain];
stack[2015] = [r3 retain];
stack[2014] = [arg4 retain];
r4 = [r2 dataUsingEncoding:0x4];
[r6 release];
r0 = [r4 retain];
asm { vld1.64 {d16, d17}, [r1]! };
asm { vld1.64 {d18, d19}, [r1] };
asm { vst1.64 {d16, d17}, [r1]! };
asm { vst1.64 {d18, d19}, [r1] };
r8 = objc_retainAutorelease(r0);
r10 = sp + 0x88;
CC_SHA1([r8 bytes], [r8 length], r10);
r7 = r7;
r11 = [[NSMutableString stringWithCapacity:0x28] retain];
r6 = 0x0;
do {
r3 = *(int8_t *)(r10 + r6);
[r11 appendFormat:@"%02x"];
r6 = r6 + 0x1;
} while (r6 != 0x14);
stack[2013] = r11;
r4 = [[stack[2015] dataUsingEncoding:0x4, r3, stack[2000]] retain];
[r8 release];
r0 = objc_retainAutorelease(r4);
r5 = r0;
CC_SHA1([r0 bytes], [r5 length], r10);
r7 = r7;
r8 = [objc_msgSend(@class(NSMutableString), @selector(stringWithCapacity:)) retain];
r6 = 0x0;
do {
r3 = *(int8_t *)(r10 + r6);
[r8 appendFormat:@"%02x"];
r6 = r6 + 0x1;
} while (r6 != 0x14);
r4 = [[stack[2014] dataUsingEncoding:0x4, r3] retain];
[r5 release];
r0 = objc_retainAutorelease(r4);
r5 = r0;
r0 = [r0 bytes];
stack[2008] = r5;
CC_SHA1(r0, [r5 length], r10);
r7 = r7;
r11 = [objc_msgSend(@class(NSMutableString), @selector(stringWithCapacity:)) retain];
r6 = 0x0;
do {
[r11 appendFormat:@"%02x"];
r6 = r6 + 0x1;
} while (r6 != 0x14);
stack[2012] = @class(NSString);
r10 = stack[2013];
r6 = [[r11 substringToIndex:0x5] retain];
r4 = [[r10 substringToIndex:0x4] retain];
r7 = r7;
r5 = [[r8 substringToIndex:0x5] retain];
r1 = @selector(stringWithFormat:);
stack[2011] = r1;
asm { strd r4, r5, [sp, #0xb8 + var_B8] };
stack[2012] = [objc_msgSend(stack[2012], r1) retain];
[r5 release];
[r4 release];
[r6 release];
r10 = [[r10 substringFromIndex:0x24] retain];
r6 = [[r11 substringFromIndex:0x23] retain];
r1 = @selector(substringFromIndex:);
r0 = objc_msgSend(r8, r1);
r7 = r7;
r0 = [r0 retain];
r5 = r0;
asm { strd r6, r5, [sp, #0xb8 + var_B8] };
asm { ldrd r0, r1, [sp, #0xb8 + var_90] };
r4 = [objc_msgSend(r0, r1) retain];
[r5 release];
[r6 release];
[r10 release];
r6 = @class(NSString);
r7 = r7;
r5 = [[ZhuLi specialSauce] retain];
stack[2010] = r4;
asm { strd r5, r4, [sp, #0xb8 + var_B8] };
r7 = r7;
r10 = [objc_msgSend(r6, stack[2011]) retain];
[r5 release];
r5 = sp + 0x47;
stack[2000] = 0x4;
[r10 getCString:r5 maxLength:0x21 encoding:stack[2000]];
r6 = malloc(0x30);
stack[2006] = sp + 0x40;
r1 = sp + 0x68;
asm { strd r6, r4, [sp, #0xb8 + var_A8] };
r2 = 0x1;
stack[2002] = r1;
stack[2003] = 0x20;
r3 = r5;
asm { strd r1, r0, [sp, #0xb8 + var_B8] };
if (CCCrypt(0x1, 0x0, r2, r3, stack[2000], stack[2001], stack[2002], stack[2003], stack[2004], stack[2005], stack[2006]) != 0x0) {
free(r6);
}
else {
r5 = [[NSData dataWithBytesNoCopy:r6 length:0x0] retain];
[[ZhuLi montyCarlo:r5] retain];
[r5 release];
}
[r10 release];
[stack[2010] release];
[stack[2012] release];
[r11 release];
[r8 release];
[stack[2013] release];
[stack[2008] release];
[stack[2014] release];
[stack[2015] release];
r0 = *___stack_chk_guard - *___stack_chk_guard;
if (r0 != 0x0) {
__stack_chk_fail();
}
r0 = loc_a55a();
return r0;
}
I inspected both assembly and pseudocode in order to simulate what was happening and got the flag! CCCrypt is using AES 128 CBC with a NULL IV according to this page.
from Crypto.Hash import SHA
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
flag1 = "cApwN{y0u_are_th3_ch0sen_1}"
flag2 = "cApwN{0mg_d0es_h3_pr4y}"
flag3 = "cApwN{1m_1n_ur_n00twork_tere3fik}"
def sha1(s):
h = SHA.new()
h.update(s)
return h.hexdigest()
hash1 = sha1(flag1)
hash2 = sha1(flag2)
hash3 = sha1(flag3)
sauce = "bler"
key = hash3[:0x5] + hash1[:0x4] + hash2[:0x5] + sauce + hash1[0x24:] + hash3[0x23:] + hash2[0x23:]
ciphertext = "\xdd\x2a\x7a\xec\xee\x8b\x7d\xec\x0e\x72\x33\xc7\x1b\xe3\xf7\x50\xfc\x4b\x7a\x85\x2c\xa0\xe1\x19\x7f\x54\x60\xd3\x16\x6d\x62\xfd" #0x435F0
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, "\x00"*16)
print(cipher.decrypt(ciphertext))
Level 5
Looks like this thing is pretty locked down, I don't think you can touch this.
Level5-69c2713162cb8f5e9418f8c08f3fa0a1ecb4928d.ipa

I started reversing the code and found a clear suggestion to sub_8D80. When we click Hammer time! the app exits. I started reversing the function sub_A180 which is called by [Level5Demo6DemoVC hammerTime:] at 0xA4E0. I found two functions interesting, because they call stat(): sub_8B5C and sub_8C2E.
sub_8B5C.c
int sub_8c2e(int arg0) {
r0 = arg0;
r4 = sp - 0x108;
asm { bfc r4, #0x0, #0x3 };
sp = r4;
r8 = r0;
memcpy(sp + 0x70, 0x138f0, 0x71);
r5 = strlen(sp + 0x70);
if (r5 != 0x0) {
r6 = sp + 0x70;
r10 = sp + 0x4;
r4 = 0x0;
do {
r0 = r4 + 0xe6;
r1 = 0x0;
do {
*(r6 + r1) = *(int8_t *)(r6 + r1) ^ r0;
r1 = r1 + 0x1;
} while (r5 != r1);
if (lstat(r6, r10) == 0x0) {
r0 = stack[1985];
if ((r0 & 0xa0) != 0x0) {
(r8)(r0);
}
}
r6 = 0x1 + r6 + r5;
r4 = r4 + 0x1;
r5 = strlen(r6);
} while (r5 != 0x0);
}
...
}
I implemented this pseudocode and the code of sub_8C2E and realized that they were checking if the device was jailbroken or not, by verifying the existence of some files.
f = open("Level5Demo")
s = f.read()
f.close()
def decodeTarget(target):
cur = 0
currentPath = ""
for i in range(0, len(target)):
if target[i] == "\x00":
print(currentPath)
cur += 1
currentPath = ""
continue
n = cur + 0xe6
currentPath += chr(ord(target[i]) ^ n)
target = s[0x13800:0x13800+0xee]
decodeTarget(target)
target = s[0x138f0:0x138f0+0x71]
decodeTarget(target)
/Applications/Cydia.app /Library/MobileSubstrate/MobileSubstrate.dylib /var/cache/apt /var/lib/apt /var/lib/cydia /var/log/syslog /var/tmp/cydia.log /bin/bash /bin/sh /usr/sbin/sshd /usr/libexec/ssh-keysign /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/apt /Library/Ringtones /Library/Wallpaper /usr/arm-apple-darwin9 /usr/include /usr/libexec /usr/share /Applications
Then I started looking at the KeychainThing class functions and realized that the app was checking if there was a given item in the Keychain.
I found the service [KeychainThing newSearchDictionary:] at 0x8754:
void * -[KeychainThing newSearchDictionary:](void * self, void * _cmd, void * arg2) {
...
[r4 setObject:*_kSecClassGenericPassword forKey:*_kSecClass];
...
r0 = [r4 setObject:@"com.uber.ctf.level5" forKey:*_kSecAttrService];
...
}
If we look again at sub_A180 it’s easy to understand that the account and password must match
int sub_a180(int arg0, int arg1) {
...
r0 = "setmeinurkeychain";
r2 = 0x0;
r4 = (extension in Foundation):Swift.String._bridgeToObjectiveC () -> __ObjC.NSString();
r2 = r4;
r7 = r7;
if ([[r6 searchKeychainCopyMatching:r2] retain] != 0x0) {
r1 = @selector(searchKeychainCopyMatching:);
asm { stmib sp, {r6, r8} };
stack[2037] = r5;
r10 = static Foundation.Data._unconditionallyBridgeFromObjectiveC ();
r0 = [r4 release];
r0 = loc_bfb0(r10, r1);
r4 = *(extension in Foundation):Swift.String.Encoding.utf8.unsafeMutableAddressor : (extension in Foundation):Swift.String.Encoding();
r0 = @class(NSString);
r5 = objc_allocWithZone();
r0 = r10;
r6 = Foundation.Data._bridgeToObjectiveC ();
r11 = [r5 initWithData:r6 encoding:r4];
r0 = r10;
r0 = sub_bd38();
r0 = [r6 release];
r5 = *0x15cf4;
if (r5 == 0x0) {
r0 = @class(NSString);
r0 = sub_9500();
r5 = swift_getObjCClassMetadata();
r0 = 0xba38;
asm { dmb };
*(0xa2bc + r0) = r5;
}
r0 = [r11 retain];
r1 = 0xc;
r2 = 0x2;
r0 = "youdidathing";
r3 = r5;
r8 = (extension in Foundation):__ObjC.NSString.init (stringLiteral : Swift.StaticString) -> __ObjC.NSString();
if (r11 != 0x0) {
stack[2039] = r11;
stack[2038] = r8;
r4 = *0x15e0c;
r0 = [r8 retain];
if (r4 == 0x0) {
r0 = @class(NSObject);
r0 = sub_9500();
r4 = swift_getObjCClassMetadata();
r0 = 0xbad0;
asm { dmb };
*(0xa33c + r0) = r4;
}
...
}
The thing is… How can we touch the Keychain? Since I didn’t have permission to jailbreak my device, I used IPAPatch to inject the following code in the app:
//
// IPAPatchEntry.m
// IPAPatch
//
// Created by wutian on 2017/3/17.
// Copyright © 2017年 Weibo. All rights reserved.
//
#import "IPAPatchEntry.h"
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@implementation IPAPatchEntry
+ (void)load
{
[self for_example_showAlert];
[self i_can_touch_this];
}
+ (void)for_example_showAlert
{
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(3 * NSEC_PER_SEC)), dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
UIAlertController * alertController = [UIAlertController alertControllerWithTitle:@"Hacked" message:@"Hacked with IPAPatch" preferredStyle:UIAlertControllerStyleAlert];
[alertController addAction:[UIAlertAction actionWithTitle:@"OK" style:UIAlertActionStyleCancel handler:NULL]];
UIViewController * controller = [UIApplication sharedApplication].keyWindow.rootViewController;
while (controller.presentedViewController) {
controller = controller.presentedViewController;
}
[controller presentViewController:alertController animated:YES completion:NULL];
});
}
+ (void) i_can_touch_this
{
NSMutableDictionary *keychainItem = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
NSString *password = @"youdidathing";
keychainItem[(__bridge id)kSecClass] = (__bridge id)kSecClassGenericPassword;
keychainItem[(__bridge id)kSecAttrGeneric] = @"setmeinurkeychain";
keychainItem[(__bridge id)kSecAttrAccount] = @"setmeinurkeychain";
keychainItem[(__bridge id)kSecAttrService] = @"com.uber.ctf.level5";
keychainItem[(__bridge id)kSecValueData] = [password dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
if (SecItemCopyMatching((__bridge CFDictionaryRef)keychainItem, NULL) == noErr) {
keychainItem[(__bridge id)kSecValueData] = [password dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
OSStatus sts = SecItemAdd((__bridge CFDictionaryRef)keychainItem, NULL);
NSLog(@"Error Code: %d", (int)sts);
}
}
I installed the patched app and clicked Hammer time! again.
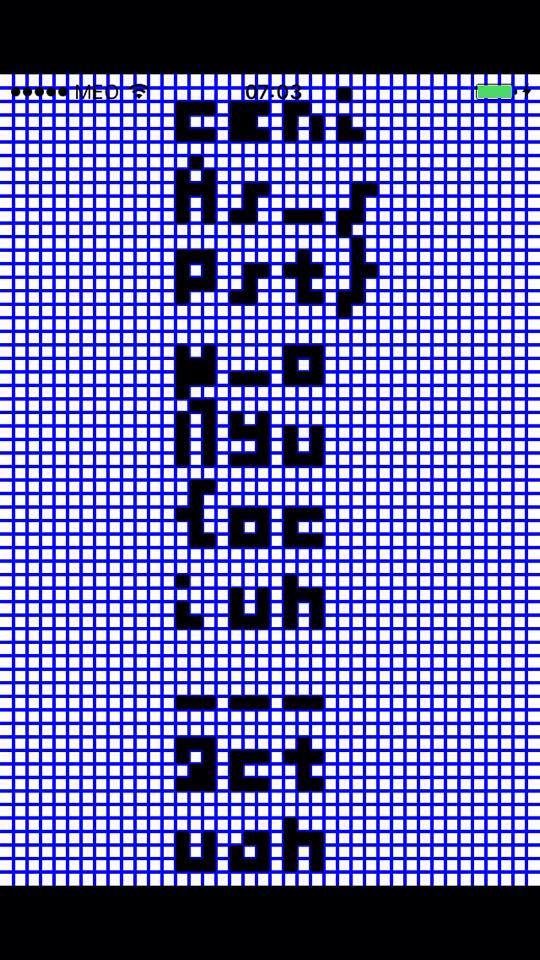
Level 6
Hey look at me im Tiny Rick! Yeah now that I got your attention, I got this app here that Squanchy squanched on my phone. Looks like there is something in there... But I don't give a @#$! I'm Tiny Rick!
Level6-679e59bdfb40233fb1359d098d7269a3320eabd2.ipa
Update: This challenge did not function properly on iOS 32bit devices, here is the updated challenge Level6-update-f0887a253daaa02e584bc9ff4edfeca1300887dc.ipa
Note: The original version of the app is still solvable. The update is only for those who wish to run the app on a 32bit device.
Update: If you are attempting to solve the 32bit challenge and running into issues, contact @suspiciousfudge on the Slack channel
In this level we can enter some text and after clicking the button we get a binary string:

I noticed that characters were mapped to binary strings, regardless of their position. For example:
"a" -> 1000
"b" -> 011100
"aaba" -> 100010000111001000
It’s easy to get the correct mapping by generating a string such as
{'0110': 's', '11101': 'n', '0010': 'r', '01110111001': 'z', '01110111000': '3', '111001001': 'V', '01110111100': '8', '01110101000': 'R', '01110101001': 'y', '01010110100': 'H', '01110111101': 'G', '01010111110': 'k', '01010111111': 'U', '010101110': 'I', '01010110101': '9', '011110': 'p', '1110011110': 'C', '1110011111': 'Q', '01110110000': 'K', '0111110': 'f', '0111111': 'q', '11010': 'm', '11011': 'o', '0101011110': 'F', '1111': 'e', '01110110001': 'J', '00110': 'd', '11100101': 'h', '01110110010': '_', '01110111011': 'Y', '01110110101': 'W', '01110110100': '{', '0101011001': 'S', '01110100': 'D', '01110111010': 'X', '01110101010': '2', '01110111111': 'w', '0100': 'l', '01110111110': 'B', '01010101': 'N', '001111': 'v', '001110': 'g', '01110101110': '0', '01110101111': '4', '011100': 'b', '01010110111': 'T', '01010110110': '5', '1110011101': 'P', '010101000': 'E', '010101001': 'j', '01011': 'c', '0111010110': 'A', '11100111001': 'O', '11100111000': '}', '01110110011': '1', '000': 'i', '0101011000': 'L', '01110110110': '7', '1100': 'u', 'x': '111001000', '01110110111': '6', '1001': 't', '1000': 'a'}
In adittion to this convertion, the app must be doing something else. Let’s analyze it statically.
I found some interesting functions at 0xA514 and 0xAE7A. sub_AE7A is called inside the first one with the following arguments: 0x154EC, 0x1, 0x154FC, 0x0, a pointer to a byte array and 0x130. Then, sub_A514 compares the same byte array with another static byte array at 0x1550C in a loop with 0x130 iterations. I used Hopper Disassembler to decompile sub_AE7A.
int sub_ae7a(int arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4, int arg5) {
sp = sp - 0xa8;
memset(sp + 0x38, 0x0 & 0xff, 0x10);
func = 0x0;
if (arg1 == 0x0) {
func = 0xb015;
}
if (arg1 == 0x1) {
func = 0xb195; //arg1 = 0x1 -> key is constructed by sub_b195
}
if ((((func != 0x0) && (arg0 != 0x0)) && (arg2 != 0x0)) && (arg4 != 0x0)) {
for (i = 0x0; i < 0x8; i = i + 0x1) {
*(i + sp + 0x38) = *(int8_t *)(i + arg2);
}
if ((arg3 & 0x3f) != 0x0) {
sub_b312(sp + 0x40, arg3 >> 0x6);
(func)(arg0, sp + 0x38, sp + 0x48);
}
for (i = 0x0; i < arg5; i = i + 0x1) {
if ((arg3 + i & 0x3f) == 0x0) { //The key is modified here!
sub_b312(sp + 0x40, arg3 + i >> 0x6);
(func)(arg0, sp + 0x38, sp + 0x48);
}
*(i + arg4) = *(int8_t *)((arg3 + i & 0x3f) + sp + 0x48) ^ *(int8_t *)(i + arg4);
}
stack[2019] = 0x0;
}
else {
stack[2019] = 0x1;
}
stack[2006] = stack[2019];
if (*___stack_chk_guard == *___stack_chk_guard) {
r0 = stack[2006];
}
else {
r0 = __stack_chk_fail();
}
return r0;
}
In fact, the byte array is modified inside sub_0xAE7A. Each byte is XORed with some key. However, it’s very hard to implement every function related with the key construction phase, because they seem complex. It’s much easier (and faster) to get what is being XORed using dynamic analysis. The plan is to get the key and XOR it with the static byte array at 0x1550C in order to get the correct input.
➜ Dynamic Analysis
I used IPAPatch to attach lldb to the app process in Xcode. First of all, I obtained the base address of the binary in order to calculate further breakpoints due to ASLR:
(lldb) image list [ 0] C665CD58-8669-3E65-B1D4-748F54F23D93 0x0007d000 /Users/andrebaptista/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/IPAPatch-alwuicstdpkmzpdcxvwfqicaiqcb/Build/Products/Debug-iphoneos/IPAPatch-DummyApp.app/Level6
Now, it’s possible to calculate any .text address like this: 0x0007d000 - 0x4000 + target_address.
(lldb) br set -a 0x83e7a Breakpoint 1: where = Level6`___lldb_unnamed_symbol18$$Level6, address = 0x00083e7a
(lldb) register read General Purpose Registers: r0 = 0x0008e4ec r1 = 0x00000001 r2 = 0x0008e4fc r3 = 0x00000000 r4 = 0x16ea9a10 r5 = 0x00000000 r6 = 0x16e61dc0 r7 = 0x003102d4 r8 = 0x16e61dc0 r9 = 0x00000130 r10 = 0x16ea3590 r11 = 0x16e61dc0 r12 = 0x16eade80 sp = 0x0031023c lr = 0x00083765 Level6`___lldb_unnamed_symbol14$$Level6 + 593 pc = 0x00083e7a Level6`___lldb_unnamed_symbol18$$Level6 cpsr = 0x60000030(lldb) x/3wx $sp 0x0031023c: 0x16eade80 0x00000130 0x00310200(lldb) x/s 0x16eade80 0x16eade80: "100010000111001000\e:`\xffffffc5\xffffffe6\x16"
After hitting the breakpoint, I inspected the 5th argument of sub_AE7A, which was the result of converting 0x16eade80). I decided to set a breakpoint at 0xafd4, where the current key byte is loaded with the instruction ldrb r0, [r0].
(lldb) br set -a 0x83fd4 Breakpoint 2: where = Level6`___lldb_unnamed_symbol18$$Level6 + 346, address = 0x00083fd4 </pre class="terminal">(lldb) register read General Purpose Registers: r0 = 0x003101dc r1 = 0x00000000 r2 = 0x00000000 r3 = 0xd0796fe7 r4 = 0x00000000 r5 = 0x00000010 r6 = 0x003101cc r7 = 0x00310234 r8 = 0xc372007f r9 = 0x00000007 r10 = 0xc372007f r11 = 0x16e61dc0 r12 = 0x0008d108 (void *)0x1c05fca1: __divsi3 + 1 sp = 0x00310194 lr = 0xc372007f pc = 0x00083fd4 Level6`___lldb_unnamed_symbol18$$Level6 + 346 cpsr = 0x60000030(lldb) x/64bx 0x003101dc 0x003101dc: 0x47 0x6f 0xb5 0x14 0x4b 0xf9 0x1e 0x83 0x003101e4: 0x00 0x23 0x6a 0x81 0xd7 0xb8 0x7f 0x3b 0x003101ec: 0x07 0x04 0xe8 0x2b 0x8b 0xfe 0xde 0xe7 0x003101f4: 0x3f 0x58 0x1d 0x0f 0xf2 0xae 0xa5 0xb8 0x003101fc: 0xdd 0x47 0x3c 0x08 0x13 0x2f 0x1d 0x53 0x00310204: 0x74 0xbd 0x30 0x98 0x1d 0x9e 0xd9 0xc1 0x0031020c: 0x7b 0xf3 0xfd 0x8c 0xda 0x16 0x10 0x51 0x00310214: 0xd4 0x87 0x10 0xa9 0x5b 0xd5 0x99 0x3b
These are the first 64 bytes of the key. I continued to debug and uncovered the first five states of the key, 320 bytes in total, which is more than enough since the length of the correct binary string is 304 bytes. Now it’s trivial to get the correct binary string:
correct-bin.py (click to expand)
key = [0x47, 0x6f, 0xb5, 0x14, 0x4b, 0xf9, 0x1e, 0x83, 0x00, 0x23, 0x6a, 0x81, 0xd7, 0xb8, 0x7f, 0x3b, 0x07, 0x04, 0xe8, 0x2b, 0x8b, 0xfe, 0xde, 0xe7, 0x3f, 0x58, 0x1d, 0x0f, 0xf2, 0xae, 0xa5, 0xb8, 0xdd, 0x47, 0x3c, 0x08, 0x13, 0x2f, 0x1d, 0x53, 0x74, 0xbd, 0x30, 0x98, 0x1d, 0x9e, 0xd9, 0xc1, 0x7b, 0xf3, 0xfd, 0x8c, 0xda, 0x16, 0x10, 0x51, 0xd4, 0x87, 0x10, 0xa9, 0x5b, 0xd5, 0x99, 0x3b, 0x9a, 0x2b, 0xcb, 0xc6, 0x21, 0x81, 0xd6, 0x60, 0x76, 0x34, 0x40, 0xaa, 0xfa, 0xe5, 0xe9, 0x12, 0x5f, 0x85, 0x09, 0x91, 0xc9, 0x19, 0x89, 0xc5, 0x25, 0x0b, 0x3d, 0x36, 0xdc, 0x54, 0xe6, 0xe5, 0xe7, 0x15, 0x18, 0x65, 0x5e, 0xe8, 0x2b, 0xf8, 0x71, 0x59, 0xa6, 0x2b, 0x66, 0xe0, 0x73, 0x6b, 0x4b, 0x2f, 0xd9, 0x08, 0x22, 0xc1, 0x45, 0xdc, 0xf0, 0x4b, 0x2e, 0x41, 0xb7, 0x3a, 0x44, 0x6f, 0x58, 0x60, 0xb1, 0x3e, 0xc5, 0x8a, 0x35, 0xb7, 0xaa, 0x59, 0x6a, 0x82, 0xb4, 0x8c, 0xbf, 0x8e, 0x6d, 0x8a, 0xfc, 0xc6, 0x3f, 0xb6, 0x60, 0x4b, 0xc8, 0x7f, 0x60, 0xc8, 0xa9, 0xf0, 0x33, 0x1f, 0x01, 0x68, 0xfe, 0xc9, 0xc1, 0x89, 0xd9, 0x12, 0xa7, 0xbc, 0xb3, 0x67, 0x67, 0xb7, 0xa9, 0x77, 0xde, 0xe7, 0xf7, 0x82, 0x86, 0xd4, 0x92, 0xcb, 0x5d, 0x67, 0xa0, 0xb4, 0x61, 0x0c, 0xc6, 0x36, 0xbc, 0x53, 0x55, 0xa9, 0x71, 0xda, 0xab, 0xc6, 0x25, 0x18, 0x9d, 0xab, 0xec, 0xd3, 0xc6, 0xc3, 0x3d, 0xb7, 0x31, 0x51, 0x38, 0xb9, 0x21, 0x9d, 0xf6, 0x93, 0x3c, 0x8f, 0x1a, 0xe3, 0xa8, 0x76, 0xdb, 0x20, 0x73, 0x97, 0xc4, 0x82, 0xae, 0x32, 0x4b, 0xb9, 0x7d, 0x6c, 0x66, 0xe9, 0xbf, 0x22, 0x16, 0xd2, 0xb1, 0xe5, 0x1b, 0x7b, 0x66, 0x49, 0xb2, 0x55, 0x7d, 0xe7, 0x07, 0xa7, 0xb0, 0x80, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x76, 0x52, 0x12, 0x2d, 0xa1, 0x43, 0x4e, 0x0d, 0xb0, 0xeb, 0xf7, 0xd0, 0x4f, 0x30, 0xfc, 0xa1, 0x46, 0x74, 0x08, 0x17, 0x47, 0xfd, 0x48, 0x1b, 0xb2, 0x06, 0xa1, 0x11, 0xbf, 0xc1, 0x50, 0x8b, 0x57, 0xc5, 0xb3, 0x7a, 0x0f, 0x80, 0xda, 0x05, 0x1a, 0xb7, 0x24, 0xde, 0x70, 0xc7, 0xc4, 0xf0, 0x38, 0xa1, 0x2c, 0xd2, 0xa9, 0x2e, 0xbc, 0x1c, 0xfe, 0xce, 0x6c, 0xe3, 0x6b, 0x42]
data1550C = [0x77, 0x5e, 0x85, 0x25, 0x7a, 0xc9, 0x2f, 0xb3, 0x31, 0x13, 0x5b, 0xb0, 0xe7, 0x89, 0x4e, 0x0b, 0x36, 0x35, 0xd9, 0x1a, 0xbb, 0xce, 0xef, 0xd6, 0x0e, 0x68, 0x2c, 0x3f, 0xc3, 0x9e, 0x94, 0x89, 0xed, 0x76, 0x0c, 0x39, 0x23, 0x1e, 0x2d, 0x62, 0x44, 0x8c, 0x01, 0xa9, 0x2d, 0xaf, 0xe9, 0xf0, 0x4b, 0xc3, 0xcc, 0xbc, 0xeb, 0x26, 0x21, 0x61, 0xe5, 0xb6, 0x21, 0x99, 0x6a, 0xe4, 0xa8, 0x0a, 0xaa, 0x1a, 0xfb, 0xf6, 0x10, 0xb1, 0xe7, 0x50, 0x47, 0x05, 0x71, 0x9b, 0xcb, 0xd5, 0xd8, 0x23, 0x6f, 0xb4, 0x39, 0xa1, 0xf9, 0x28, 0xb9, 0xf5, 0x14, 0x3b, 0x0c, 0x06, 0xed, 0x65, 0xd7, 0xd4, 0xd6, 0x25, 0x29, 0x54, 0x6e, 0xd9, 0x1b, 0xc8, 0x40, 0x68, 0x97, 0x1b, 0x57, 0xd1, 0x43, 0x5b, 0x7b, 0x1e, 0xe9, 0x39, 0x13, 0xf0, 0x75, 0xed, 0xc1, 0x7b, 0x1e, 0x71, 0x86, 0x0a, 0x75, 0x5e, 0x68, 0x50, 0x80, 0x0f, 0xf4, 0xba, 0x04, 0x86, 0x9a, 0x69, 0x5a, 0xb3, 0x84, 0xbd, 0x8e, 0xbf, 0x5d, 0xbb, 0xcd, 0xf6, 0x0f, 0x86, 0x51, 0x7b, 0xf9, 0x4e, 0x51, 0xf8, 0x98, 0xc1, 0x03, 0x2e, 0x30, 0x58, 0xce, 0xf8, 0xf0, 0xb9, 0xe9, 0x23, 0x97, 0x8d, 0x83, 0x56, 0x56, 0x86, 0x98, 0x46, 0xee, 0xd7, 0xc6, 0xb2, 0xb6, 0xe4, 0xa3, 0xfb, 0x6c, 0x57, 0x91, 0x85, 0x51, 0x3d, 0xf6, 0x07, 0x8c, 0x62, 0x65, 0x98, 0x41, 0xeb, 0x9a, 0xf6, 0x14, 0x28, 0xac, 0x9b, 0xdd, 0xe2, 0xf7, 0xf3, 0x0c, 0x86, 0x01, 0x60, 0x09, 0x89, 0x11, 0xac, 0xc6, 0xa2, 0x0c, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0xd2, 0x99, 0x47, 0xeb, 0x11, 0x43, 0xa7, 0xf5, 0xb3, 0x9e, 0x02, 0x7b, 0x89, 0x4c, 0x5c, 0x57, 0xd9, 0x8e, 0x13, 0x27, 0xe3, 0x80, 0xd5, 0x2a, 0x4a, 0x56, 0x78, 0x82, 0x64, 0x4c, 0xd6, 0x36, 0x96, 0x81, 0xb1, 0xf1, 0x0e, 0x47, 0x63, 0x23, 0x1c, 0x90, 0x72, 0x7f, 0x3c, 0x81, 0xda, 0xc6, 0xe1, 0x7e, 0x01, 0xcd, 0x90, 0x77, 0x45, 0x39, 0x26, 0x76, 0xcc, 0x79, 0x2a, 0x83, 0x37, 0x90, 0x20, 0x8e, 0xf0, 0x61, 0xba, 0x66, 0xf4, 0x82, 0x4a, 0x3e, 0xb1, 0xeb, 0x35, 0x2b, 0x87, 0x15, 0xee, 0x40, 0xf7]
correctBin = ""
for i in range(len(data1550C)):
correctBin += chr(data1550C[i] ^ key[i])
print(correctBin)
0101101010110110111100111010101101010101011101010010101011101111010010101111101101000100101011111011010011101100010111011000101100111011000101110110001011101101100110010101111100100010101101010101011010101110110110010101111101001100001010111110110101111111111111111111111111111111111111111111101110101000
Then, something went wrong. I converted the binary back to string and I obtained
correctBin = "0101101010110110111100111010101101010101011101010010101011101111010010101111101101000100101011111011010011101100010111011000101100111011000101110110001011101101100110010101111100100010101101010101011010101110110110010101111101001100001010111110110101111111111111111111111111111111111111111111101110101000"
d = {'01110100001': 'H', '01110100000': 'W', '0110': 's', '0111010010': 'L', '11100100100': 'R', '0010': 'r', '01010111011': '1', '01010111010': '9', '111001000': 'x', '010100': 'v', '01110101001': '{', '010101100': 'I', '01010111110': '_', '01010111111': 'Z', '01110101101': 'K', '01110101100': '8', '01010110100': 'X', '01010110101': '0', '011110': 'p', '0111110': 'f', '0111111': 'q', '1111': 'e', '0101011011': 'A', '11100100101': 'O', '11010': 'm', '11011': 'o', '01110110000': 'B', '01110110001': '3', '00110': 'd', '01010101': 'N', '01110110100': 'z', '111000': '.', '1000': 't', '11101': 'n', '11100111': 'M', '01110100010': 'J', '01110100011': '4', '01110101011': 'w', '01110101010': 'y', '0100': 'l', '111001010': 'V', '01110110101': '5', '001111': ',', '001110': 'g', '01110101110': 'U', '01110101000': '}', '01010111101': 'Y', '01010111100': '6', '011100': 'b', '01110110010': '7', '1110010110': 'j', '1110010111': 'Q', '010101000': 'C', '010101001': 'E', '01011': 'c', '0101011100': 'F', '01110110011': '2', '000': 'i', '1110010011': 'P', '1001': 'a', '1100': 'u', '11100110': 'h', '01110111': 'D', '01110110111': 'G', '0111010011': 'S', '01110110110': 'k', '01110101111': 'T'}
flag = ""
i = 0
while i < 0x130:
for key in d.keys():
if correctBin.find(key, i) == i:
flag += d[key]
i += len(key)
break
print(flag)
Thanks @suspiciousfudge for this awesome challenge!